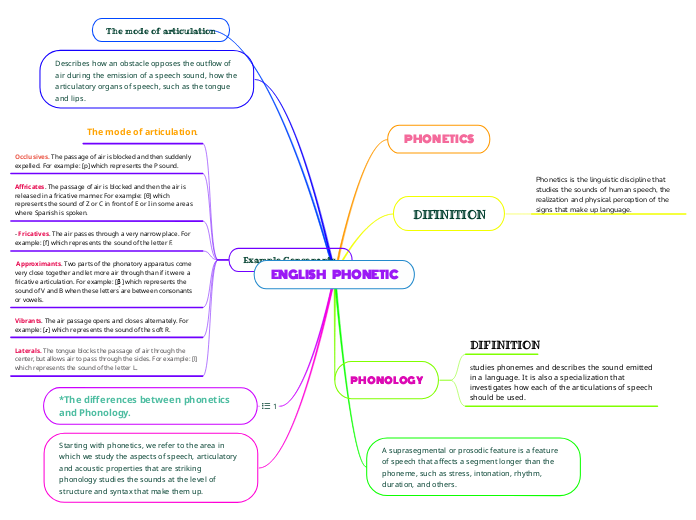
ENGLISH PHONETIC
PHONETICS
DIFINITION
Phonetics is the linguistic discipline that studies the sounds of human speech, the realization and physical perception of the signs that make up language.
PHONOLOGY
DIFINITION
studies phonemes and describes the sound emitted in a language. It is also a specialization that investigates how each of the articulations of speech should be used.
A suprasegmental or prosodic feature is a feature of speech that affects a segment longer than the phoneme, such as stress, intonation, rhythm, duration, and others.
The mode of articulation
Describes how an obstacle opposes the outflow of air during the emission of a speech sound, how the articulatory organs of speech, such as the tongue and lips.
Example Consonants
Occlusives. The passage of air is blocked and then suddenly expelled. For example: [p] which represents the P sound.
Affricates. The passage of air is blocked and then the air is released in a fricative manner. For example: [θ] which represents the sound of Z or C in front of E or I in some areas where Spanish is spoken.
- Fricatives. The air passes through a very narrow place. For example: [f] which represents the sound of the letter F.
Approximants. Two parts of the phonatory apparatus come very close together and let more air through than if it were a fricative articulation. For example: [β̞] which represents the sound of V and B when these letters are between consonants or vowels.
Vibrants. The air passage opens and closes alternately. For example: [ɾ] which represents the sound of the soft R.
Laterals. The tongue blocks the passage of air through the center, but allows air to pass through the sides. For example: [l] which represents the sound of the letter L.