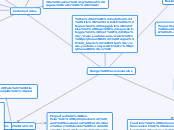
Hange Macromolecules
Proteins
Monomers: Amino Acids
Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen
Functions: Hormones, movement, immune system, enzymes, and transport
Examples: Muscles, Fingernails, skin, and Hair
Properties: have four tiers that fold on themelves.

lipids(fat)
Monomers: triglycerides
Carbon, Oxygen, and Hydrogen
Functions: energy storage, cushion organs, and insulates body
Examples: Fats, Oils, Phospholipids, and Steroids
Properties: Non-Polar, Hydrophobic, and Unsaturated Fats are are double bonds in fatty chains, and liquid at room temp and Saturated Fat are all carbon bonded, No double bonds, and solid at room temp.

Carbohydrates
Monomers: Monosaccharides
Carbon, Oxygen, and Hydrogen
Functions: quick energy, energy storage, and structure
Examples: Glucose, starches, Cellulose, and Glycogen
Properties: Structure is a carbon ring and sugars ratio 1:2:1
Nucleic Acids
Monomers: Nucleotide
Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus
Functions: Series of bases encodes information, and Stored information is passed from parent to offspring
Examples: RNA and DNA
Properties: DNA is a double helix and RNA is a single chain