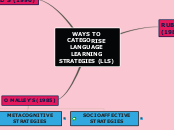
WAYS TO CATEGORISE LANGUAGE LEARNING STRATEGIES (LLS)
RUBIN'S (1987)
Learning Srategies
Cognitive Learning
Metacognitive Learning
Communication Strategies
Social Strategies
OXFORD'S (1990)
Direct Strategies
Compensation
Cognitive
Memory
Indirect Strategies
Metacognitive
Affective
Social
O MALLEY'S (1985)
COGNITIVE STRATEGIES
METACOGNITIVE STRATEGIES
SOCIOAFFECTIVE STRATEGIES