N
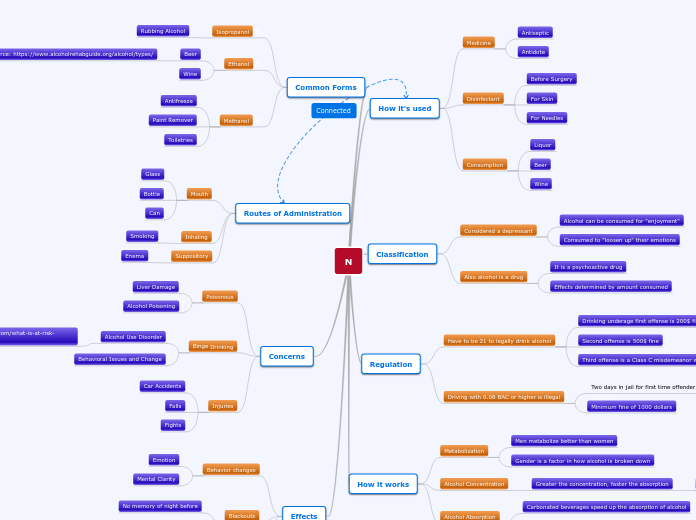
How it's used
Medicine
Antiseptic
Antidote
Disinfectant
Before Surgery
For Skin
For Needles
Consumption
Liquor
Beer
Wine
Classification
Considered a depressant
Alcohol can be consumed for "enjoyment"
Consumed to "loosen up" their emotions
Also alcohol is a drug
It is a psychoactive drug
Effects determined by amount consumed
Regulation
Have to be 21 to legally drink alcohol
Drinking underage first offense is 200$ fine
Second offense is 500$ fine
Third offense is a Class C misdemeanor with 200$ fine
Driving with 0.08 BAC or higher is illegal
Two days in jail for first time offender
Minimum fine of 1000 dollars
How it works
Metabolization
Men metabolize better than women
Gender is a factor in how alcohol is broken down
Alcohol Concentration
Greater the concentration, faster the absorption
Alcohol Absorption
Carbonated beverages speed up the absorption of alcohol
Having food in the stomach slows down absorption
Common Forms
Isopropanol
Rubbing Alcohol
Ethanol
Beer
Wine
Methanol
Antifreeze
Paint Remover
Toiletries
Routes of Administration
Mouth
Glass
Bottle
Can
Inhaling
Smoking
Suppository
Enema
Concerns
Poisonous
Liver Damage
Alcohol Poisoning
Binge Drinking
Alcohol Use Disorder
Behavioral Issues and Change
Injuries
Car Accidents
Falls
Fights
Effects
Behavior changes
Emotion
Mental Clarity
Blackouts
No memory of night before
No recollection of events
Slurred speech
Weakness in muscles used for speech
Difficult to read
Marijuana
Effects
Sense of relaxation
Relieves emotions causing a calm nature
heightened sensory perception
Seeing brighter colors
Enhanced hearing
How it works
Inhalation
THC goes directly to the lungs
Consumption
Blood absorbs THC in the bloodstream
Concerns
Brain Development
Impairs thinking and memory along with learning functions
Increased Heart attack risk
Heart rate increases for 3 hours after smoking
Regulations
Legal recreational use in Oregon
Allowed to grow up to four plants on property
21 years is the age where use is legal
Under 21 use of marijuana recreationally is illegal
Classification
Depressant
Slows down messages between brain and body
Hallucinogenic
Causes hallucinations and delusions
Routes of Administration
Inhalation
Smoking
Consumption
Edibles and Candies
Common Forms
Traditional Marijuana
Dried Flowers of a cannabis plant
Hashish
Made of resin extracted from plant then dried and compressed, stronger than traditional
How its Used
Medically
Uses marijuana extract to treat certain illness symptoms
Recreationally
Taken on an occasional basis for enjoyment
Caffeine
Effects
Increased Alertness
Decreases feeling of being tired
Increased energy
More productivity in the mornings/when working
How it works
Fools Adesonine receptors
Fakes the receptors to feel like we arent tired
Causes blood vessels to dilate
Lets more oxygen into organs during sleep
Concerns
Increased heart rate
Higher risk of a heart attack occuring
Nervousness
Makes people have the "jitters" after using
Regulations
Safe for up to 400 mg consumed a day
Still has an increase of health issues
Products not required to list how much caffeine it has
Can be confusing for people if they are limited in amount
Classification
Stimulant
Increases the activity of the central nervous system
Can be addictive
Enhances dopamine in the brain
Routes of Administration
By mouth
Coffee, energy drinks
insufflation
Blowing caffeine into body cavity
Common Forms
Natural
Seeds, leaves, nuts, berries
Synthetic
Familiar foods, coffee, tea, etc
How its Used
Restore alertness and activity
Reduces tiredness and drowsiness
In teas, coffee, energy drinks
Consumed for taste as well as a boost to the day
Tobacco
Effects
Feelings of Relaxation
Calms down inner nervous system
Increased alertness and concentration
Initial stimulation then calmness of the body after
How it Works
Nicotine flows through bloodstream into the brain
Causes the drug to kick in
Stimulation causes increase in heart rate
Also increase in blood pressure and respiration
Concerns
Can cause cancer
Lung cancer most common, can happen from repeated use
Can cause heart disease
Constant use causes blood clots and high risk of stroke
Regulations
Tobacco regulated by FDA in 2009
Can get a MIP if caught underaged
Minimum age of 18 to purchase tobacco
People want the age to increase of conumption to increase
Classification
Stimulant
Increases central nervous system activity
Depressant
Causes calming factor after initial stimulant
Routes of Administration
Inhalation
Smoking
Consumption
Through a form called "chew" usually put in lower lip
Common Forms
Smokeable Tobacco
Cigars, cigarettes, E-cig
Non smokeable Tobacco
Chew, Dry snuff
How Its Used
Used for smoking
Can also be consumed for recreational use
Can be consumed as a medicine
Promotes a persons well being
Inhalants
Effects
Slurred Speech
Lack of Coordination while speaking
Hallucinations and Delusions
Memory impairment
How it Works
Dilate and relax blood vessels
Causes initial rapid high
Initial excitation or rapid high
Then drowsiness and lightheadedness
Concerns
Slows down central nervous system
Then causes weakness and alcohol like symptoms
Feel less self conscious
Start to lose control of yourself
Regulations
38 states have placed restrictions on inhalants
Other states have it as legal for recreational use
Some states prohibit use of nitrous oxide
If you are caught then you will be fined or serve time in prison or both
Classification
Depressant
Slows down messages to the central nervous system
Can be addictive
Mostly after continued use of inhalant
Routes of Administration
Inhalation
Usually through the container of the drug
Snorting
Administered through the nose directly
Common Forms
Aerosols
Haze or air pollutants
Gases
Gasoline can be used as inhalant
How its Used
For a rapid high feeling
Usually used by younger teens
Then a calm factor after rapid hiigh
Feel drowsy after the high wears off
Meth
Effects
Extremely high body temperature
Can pass out or die because of high temp.
Paranoia
May see or hear things that aren't there
How it Works
Makes you feel extra energized
Heightens central nervous system action
Creates more chemical dopamine in your brain
Changes the way the brain works
Concerns
Long term violent behavior
Multiple killings have been linked to meth
Psychotic symptoms
hallucinations and delusions
Regulations
Dealing meth will result in a felony
No matter what it is a felony but it depends on what level
Possession of small amounts are decriminalized
Loosening laws in terms of small amounts
Classification
Stimulant
Speeds up nervous system senses
Addictive
Feel sick when you stop using meth, causes user to continue to use it
Routes of Administration
Inhalation
Smoking through a glass pipe or regularly
Snorting
Through the nose using the powdered version
Common Forms
Crystalline powder
Still very dangerous, more accessible
Shiny glass form
Highly purified crystal meth, extremely dangerous
How its Used
Can actually treat ADHD
Also can treat obesity problems
For a significant High
Used recreationally for the effects or the" high"
Opioids
Effects
Sedation
Makes user very tired or drowsy after use
Nausea
Caused by stomach irritation after use
How it Works
Attach receptors to the brain
Also attach tospinal cord and gut
Block pain messages going to the brain
The opioid receptors cause this
Concerns
Increased doses based on dependence
Need more doses to achieve same high
Cold flashes with goosebumps
Lowers temperature
Regulations
Many states now have prescription limit on opioids
Multiple laws enforced in 2018
Limit the misuse of opioids
Thousands of people misuse opioids each year
Classification
Can be addictive
After long term use, can develop addiction
Accessible
Easy to acquire and misuse
Routes of Administration
Oral
Fentanyl
Intravenous
Usually with a needle
Common Forms
Natural
Morphine, codeine
Synthetic
oxycodone, hydrocodone
How its Used
Pain killer
To relieve pain from major surgeries
Recreationally
For the "high"
Psychedelics
Effects
Increased blood pressure
Also increases body temp.
Dizziness
Drug slows down your system
How it Works
Alter users mood
Alters senses and perception
Puts receptors in the brain cortex to cause the effect
Triggered by serotonin
Concerns
Speech problems
Usually after extensive use of the drug
Memory loss
Can lead to depression and suicidal thoughts
Regulations
Became illegal in 1970
Law proposed by President Nixon
1 year in prison
If caught possessed with LSD
Classification
Psychoactive
Affects the brain and alters mood
Not necessarily addictive
Dont alter brain chemistry
Routes of Administration
Intravenous
Usually through a needle
Oral
Shrooms can be consumed by the mouth
Common Forms
Classic
LSD
Dissociative
PCP
How its Used
Recreationally
For the effect that it alters mood and senses
Therapy
Shown to help with mood and battle depression