Pathogens and immunity
pathogens
microorganism that cause disease
kwnon as infection
passed from one person to another
transmissible diseases
direct transmission
between an infected person and an undifected one
person who has the parhogen: HOST
contagious diseases
AIDS (hiv)
fungus
indirect transmission
Through the respiratory passages
viruses are propelled into the air in tiny droplets pf moisture
speaks, coughs, sneezes
breathe the droplets, become infected
touch a surface and then put them into the face
In food or water
through the alimentary canal
salmonella
food poisoning
fresh food should be washed
cooking destroys bacteria
transmityed in water
poliomyelitis
cholera
By vectors
organism that carries a pathogen from a host to another
anopheles mosquitoes
malaria
dogs, skunks, raccoons, bats
rabies
female mosquitoes
plasmodium
Body defenses
natural defences
Mechanical barriers
skin
has keratin, that is difficult to penetrate
when it is cut
blood clots seam the wound
Chemical barriers
sticky mucus
cilia sweep the mucus back up to the throat
hydrochloric acud is secreted
the ones that go through are destroyed by White blood cells
by phagocytosis
by producing antibodies
vaccination
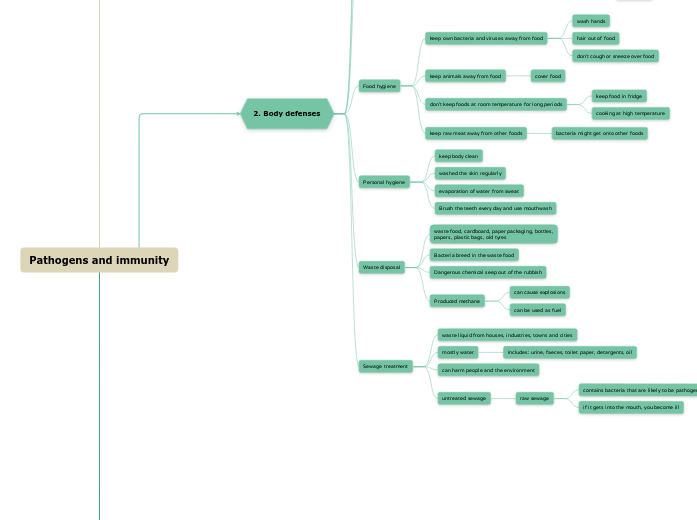
Food hygiene
keep own bacteria and viruses away from food
wash hands
hair out of food
don't cough or sneeze over food
keep animals away from food
cover food
don't keep foods at room temperature for long periods
keep food in fridge
cooking at high temperature
keep raw meat away from other foods
bacteria might get onto other foods
Personal hygiene
keep body clean
washed the skin regularly
evaporation of water from sweat
Brush the teeth every day and use mouthwash
Waste disposal
waste food, cardboard, paper packaging, bottles,
papers, plastic bags, old tyres
Bacteria breed in the waste food
Dangerous chemical seep out of the rubbish
Produced methane
can cause explosions
can be used as fuel
Sewage treatment
waste liquid from houses, industries, towns and cities
mostly water
includes: urine, faeces, toilet paper, detargents, oil
can harm people and the environment
untreated sewage
raw sewage
contains bacteria that are likely to be pathogens
if it gets into the mouth, you become ill
immune systema
lymphocytes produce antibodies to destroy pathogens
these are only produce when a pathogen is detected
when it enters the body, it meets with lymphocytes
the lymphocytes will start to divide by mitosis making a clone of lymphocytes that will secret antibodies to destroy the pathogen
while the lymphocytes do this, the pathogens breeds making you ill
inmune response
Antibodies
is a protein molecule that its shape fits right into the antigen to destroy it
the antibodies alert the phagocytes do that they would come and kill them
the antibodies sart off a series of reactions in blood that produce enzymes to digest phatogens
Memory cells
when the lymphocyte clones itself, it goes to the blood or other parts of the body
memory cells
if the same patjogen gets in the body the memory cells will be ready and kill it before it does any harm
inmune
Vaccination
inmunise people against diseases
contains weakened or dead viruses that normally causes diseases
when it enters the body, it will be recognise by lymphocytes that makes antibodies that lock with the antigens
also making memory cells to have long-term inmunity
Avtive and passive immunity
Active inmunity
make your own antibodies and memory cells
by having the diseases and getting over it
vaccinated
long-lasting
Pasive inmunity
given antibodies by another organism
injected with antibodies made by another organism
lasts for a short time
auto-immune diseases
lymphocytes can confuse our own cells with pathogens
type 1 diabetes
in some people their inmune system attacks the betas cells, in the pancreas, and destroys them
stops producing insulin