Project #3 Math 252
Circles
Area- II r^2
Radius- Half of the circumference
Circumference- 2IIr
Area
Rectangle- length x width
parallelogram- base x height
triangle- 1/2 base x height
trapeziod- 1/2 (base a + base b)h
Geometric Figures
To find the faces of prisims you look for the two shapes that are the same and perpendicual to the parallel sides
Naming the shapes- 1. The shape of the base 2. if it has right angle or oblique 3. what is the overall shape ex) pentagonal right prism When working with cones or pyramids if the center of the cone or pyramid is directly in the center of the base then it is a right triangle. If it is to the side then it is oblique.
Sum of angle measures- (n-2)180 degrees When trying to find one interior angle you do (n-2)180 degrees/n n being the # of sides
Quadadrilateral- trapezoid, parallelogram, rhombus, rectangle, square, kite
Regular Polygons- equilaterial triangle, square, pentagon, hexagon, heptagon, octagon, nonagon, decagon
Circle- semi-circle, sphere, cylinder, cone
Volume
Prism- length x width x height or Bh
Pyramid- 1/3 Bh
Cone- 1/3 II r^2h
Cylinder- Bh
B= length times with or the area of the base

Subtopic
Triangles
Pythagorean Theorem- a^2 + b^2= c^2 This only works for right angles.
Scalene- no sides are the same
Isosceles- at least two sides are the same
Equilateral- all sides the same
All angles must equal 180 degrees
Perimeter
you add up all the sides for all shapes
circle- 2IIr
Angles
Supplementary- 2 angles added together=180
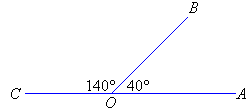

Corresponding- same angle but on different lines
Vertical- angles that are the same but across from each other
Complementary- add up to 90 degrees
Congruent- opposite angles on different lines
Acute- less than 90 degrees Obtuse- more than 90 but less than 180 a right angle is exactly 90 degrees
Surface Area
Prisms and cylinder- 2B + ph
Pyramid- B + 1/2 ps
Cone- II r^2 +rs
Sphere- 4II r^2

Subtopic