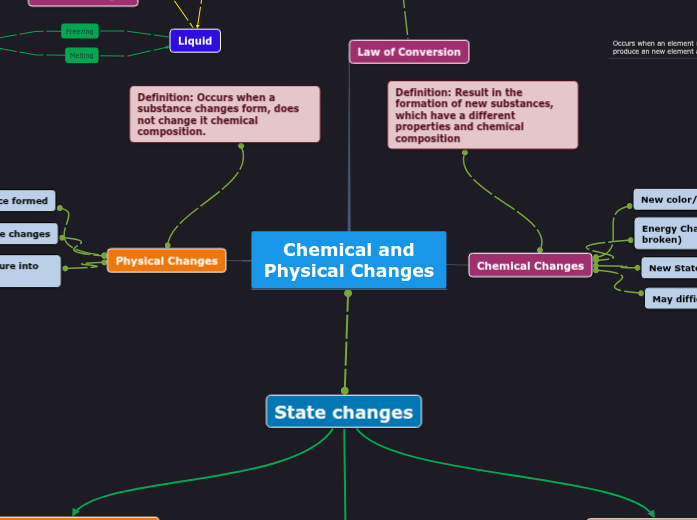
Chemical and Physical Changes
Law of Conversion
Chemical Changes
Physical Changes
Definition: Occurs when a substance changes form, does not change it chemical composition.
Definition: Result in the formation of new substances, which have a different properties and chemical composition
No new substance formed
A phase changes
Used to separate a mixture into pure
New color/ New smell
Energy Changed (Bond form or broken)
New State
May difficult to reverse
When a system is closed the mass of the reactants always equals the mass of products
Liquid
Solid
Gas
Phase Changes
State changes
Small Covalent molecules
Usually Gases unless its water
Water is produced as a gas in combustion
HF is also Hydrogen-Bonds, you can use it as l or g
Pure NH3 is gas in room tempture
Ionic Compounds
When no water its solid
Other only dissolve lightly, which forms a heterogenous mixture.
These compounds are low solubility so it will be solid (s)
Many solution involve mixing, which means water is present.
Ionic compound dissolving completely in the water which forms homogeneous solution
These compounds are soluble and it will be aqueous (aq)
Organic Compounds
Functional groups are mostly liquid
Hydro Carbons
1-4 Carbon = Gas
5-15 Carbon = Liquid
16+ Carbon = Solid
Solubility
Soluble = aqueous
Low solubility = solid
Prediction products
Synthesis
When two or more reactants combine to make one product
A+B = AB
Decomposition
When one reactant break down to two or more product.
AB = A+B
Combustion
Involving burning a substance with Oxygen
AB+O2 =CO2+H2O
Double Replacement
Occurs two Ionic compounds reacts together
AB+CD = AD+CB
Single Replacement
Occurs when an element reacts with a compound to produce an new element and compound
A+BC = B+AC
Energ Changes
Energy is measured in Joules (J) often kilo joules (KJ)
1000J = 1kj
Breaking Bonds/Attraction: Energy is required
Making Bonds/Attraction: Energy is released
A change or transfer in energy are called the Heat, or enthalpy, the symbol for enthalpy is ΔH
Endothermic Reaction
More energy is required to break the bond than released when new bond is formed
+ ΔH
Less energy in the environment
H is at the Reactants
Exothermic Reaction
More energy is released to make the bond than required when new bond is formed
- ΔH
Gain energy in the environment
A+B → C+D ΔH= +KJ
A+B+Energy = C+D
A+B → C+D ΔH= -KJ
A+B = A+B+Energy
S
L
G
Release energy to let particals ties together and put in more energy to let it break
Phase change diagrams
Precipitation reaction
Neutralization Reaction
Potential Energy
Stored Energy
Energy is stored in bonds and inter molecular forces of attraction. During the plateau inter molecular forces of attraction are changing therefore PE changes
Kinetic Energy
Movement
State
Phase
Boiling Point
Melting Point

Increasing KE = +
KE only changes during the slope of the phase change diagram. At this time all of heat added isused to speed up particles
Increasing KE = 0
Phase will change with melting and boiling point at this time heat is still adding in but temperature does not change so KE is constant. Change in phase does not involve change in KE
Potential Energy Diagram

Diagram
Produce a precipitate or solid
When an acid reacts with base, it forms an ionic compound and water
Example of salts
NaCl
KI
MgSo4
Ionice Solid
THe ionic solid is made up by Cation and Anion