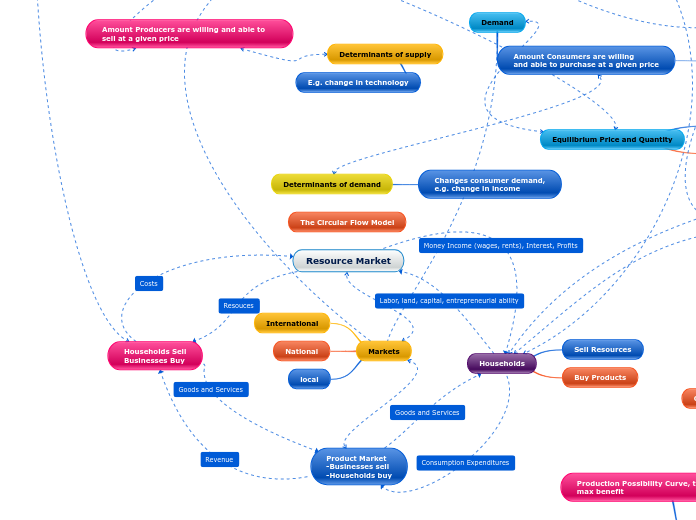
Resource Market
Opportunity Cost
Utility at the cost of other utility
Utility=Happiness
Marginal Analysis
How we Maximize Utility on the Margin
Marginal Benefit
Marginal Cost
Law of increasing opportunity costs
Households Sell
Businesses Buy
Households
Sell Resources
Buy Products
Product Market
-Businesses sell
-Households buy
The Circular Flow Model
Markets
International
National
local
Demand
Amount Consumers are willing
and able to purchase at a given price
Law of diminishing marginal utility
Supply
Determinants of demand
Changes consumer demand,
e.g. change in income
Amount Producers are willing and able to sell at a given price
Determinants of supply
E.g. change in technology
Equilibrium Price and Quantity
Price floors
Surplus=Qs-Qd
Price Ceilings
Shortage=Qd-Qs
The Government
Fiscal Policy
Changes in taxes
Changes in Government Spending
Designed for
encouraging growth in the economy
controlling inflation
encouraging full-employment
Expansionary policy
Decreases taxes, increases spending
for use in recessions
Creates deficit
Contractionary Policy
Increases taxes, decreases spending
For demand-pull inflation
creates surplus
Problems
Recognition Lag
Administrative Lag
Operational lag
political cylces/interests
Government Debt/Surplus
The Federal Reserve
Manages inflation
Prints Money
Sets Reserve Requirement
Lends money to banks
Manages interest rates
Scarcity
Economizing Problem= limited income, unlimted wants
Wants always exceed production
There is no Free Lunch
Choice must be made
Production Possibility Curve, to determine max benefit
PPC increase with international Trade
GDP
Nation's aggregate output
Expenditure Approach
GDP=C+Ig+G+Xn
Income Approach
GDP gap= Actual GDP-Potential GDP
Net Domestic Product
National Income
Personal Income
Disposable income
Household Spending
Inflation
=General rise in Price Level
Consumer Price Index
CPI goes down as inflation goes up
Cost-Push and Demand Pull Driven
Business Cycle
Prices "Sticky" Downwards
In Recessions, leads to unemployment
Peak
Recession
Unemployment
Unemployment rate
=unemployed/labor forcex100
three types
Structural
Frictional
Cyclical
Trough
Expansion
Monetary Policy
Open Market Operations
Buying and selling bonds
Influences money supply
When fed sells securities, commercial bank reserves are reduced
Repos and reverse repos
Reserve Ration
Multiplier
Discount Rate
Last case scenario
Interest on Reserves
Expansionary Monetary Policy
Feds Buy Bonds, lower the interest ratio, decrease the discount rate, etc.
increases excess in reserves, decreases the funds rate
this increases the money supply, interest rate falls
investment spending increases, AD increases, GDP increases
Restrictive Monetary Policy
Feds sell Bonds, increase the reserve ratio, increase the discount rate, etc.
excess funds rate increases, reserves decrease
money supply shrinks and interest increases
investment spending decreases, AD decreases
Inflation decreases
Federal reserve Banks
Commercial Banks
Thrift Institutions
The Public
Money
Functions of Money
Money is Liquid
Store of Value
Unit of Account
Used to buy and sell goods
M1
Currency
Checkable Deposits
M2
M1
near monies
MMDAs
MMMFs
Small denominated time deposits
Interest Rates
Demand for Money
Inversely related to bond prices
Trade
Comparative advantage
Terms of trade
Case for Trade
Prices for consumers go down
Standard of living increases
more products available for consumers
Resource Endowment
Labor-intensive
Land intensive
Capital intensive
Trade agreements
EU
WTO
NAFTA
GATT
Tariffs
Revenue tariff
protective tariff
Decreases consumption
Import Quotas
places a hard limit on incoming imports
World Price
WP>Domestic, Export
WP<Domestic, Import
Aggregate Supply (AS)
Total real output produced at each price level
changed via changes in production costs, productivity, etc.
Aggregate Demand (AD)
Real GDP desired at each price level
Determinants of aggregate Demand
Changes in C,I,G,Xn
Multiplier effect
Lowers with recession
Federal Reserve lowers interest rate
Fed Gov't begins Fiscal SPending
As G increases, AD increase
As G decreases, AD decreases