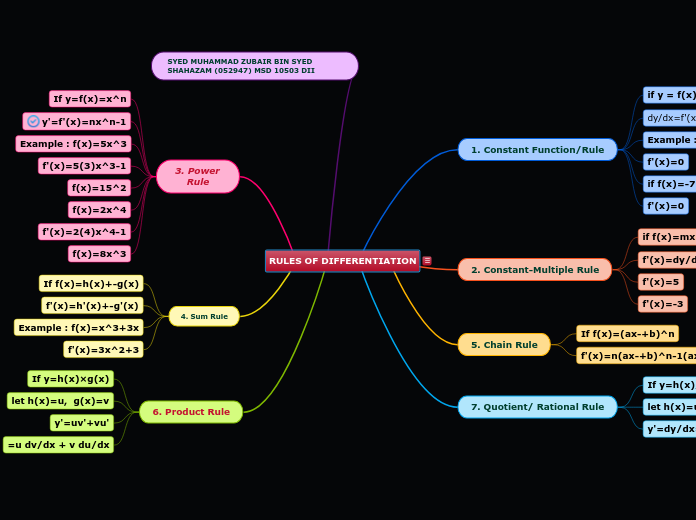
RULES OF DIFFERENTIATION
1. Constant Function/Rule
if y = f(x)=c
where C is any constant
dy/dx=f'(x)=0
Example : 1. if f(x)=4
f'(x)=0
if f(x)=-7
f'(x)=0
2. Constant-Multiple Rule
if f(x)=mx
Where m is any constant
f'(x)=dy/dx=m
f'(x)=5
f'(x)=-3
5. Chain Rule
If f(x)=(ax-+b)^n
f'(x)=n(ax-+b)^n-1(ax-+b)'
7. Quotient/ Rational Rule
If y=h(x)/g(x)
let h(x)=u, g(x)=v
y'=dy/dx=vu'-uv'/v^2
SYED MUHAMMAD ZUBAIR BIN SYED SHAHAZAM (052947) MSD 10503 DII
3. Power Rule
If y=f(x)=x^n
y'=f'(x)=nx^n-1
Example : f(x)=5x^3
f'(x)=5(3)x^3-1
f(x)=15^2
f(x)=2x^4
f'(x)=2(4)x^4-1
f(x)=8x^3
4. Sum Rule
If f(x)=h(x)+-g(x)
f'(x)=h'(x)+-g'(x)
Example : f(x)=x^3+3x
f'(x)=3x^2+3
6. Product Rule
If y=h(x)×g(x)
let h(x)=u, g(x)=v
y'=uv'+vu'
=u dv/dx + v du/dx