PLANTAIN
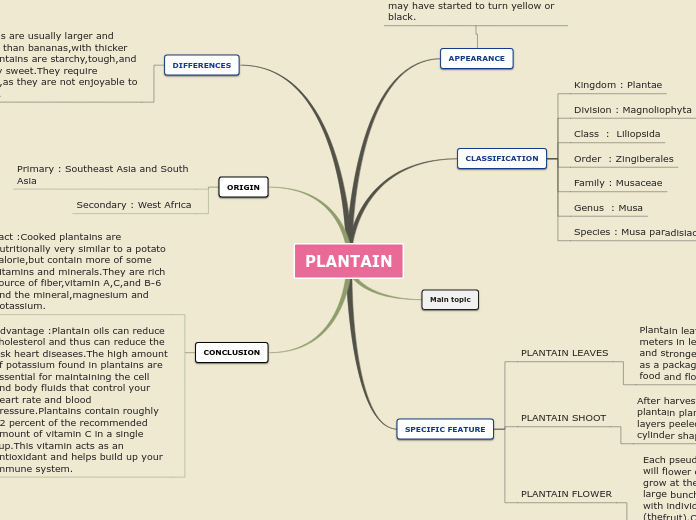
APPEARANCE
They are bigger,bright green,and thick skinned.The interior color of the fruit remains creamy and white to yellow in color.When they are ripe,they will still be green in color.When they are overripe,they may have started to turn yellow or black.
CLASSIFICATION
Kingdom : Plantae
Division : Magnoliophyta
Class : Liliopsida
Order : Zingiberales
Family : Musaceae
Genus : Musa
Species : Musa paradisiaca
Main topic
SPECIFIC FEATURE
PLANTAIN LEAVES
Plantain leaves are exceed two meters in length.They are larger and stronger.They also widely used as a packaging material for packing food and flowers.
PLANTAIN SHOOT
After harvesting the fruit.The plantain plant can be cut anf the layers peeled like an onion to get a cylinder shaped soft shoot.
PLANTAIN FLOWER
Each pseudostem of a plantain plant will flower only once.All the flowers grow at the end of its shoot in a large bunch made of multiple hands with individual fingers (thefruit).Only the first few hands will become fruits
DIFFERENCES
Plantains are usually larger and tougher than bananas,with thicker skin.Plantains are starchy,tough,and not very sweet.They require cooking,as they are not enjoyable to eat raw.
ORIGIN
Primary : Southeast Asia and South Asia
Secondary : West Africa
CONCLUSION
Fact :Cooked plantains are nutritionally very similar to a potato calorie,but contain more of some vitamins and minerals.They are rich source of fiber,vitamin A,C,and B-6 and the mineral,magnesium and potassium.
Advantage :Plantain oils can reduce cholesterol and thus can reduce the risk heart diseases.The high amount of potassium found in plantains are essential for maintaining the cell and body fluids that control your heart rate and blood pressure.Plantains contain roughly 32 percent of the recommended amount of vitamin C in a single cup.This vitamin acts as an antioxidant and helps build up your immune system.