TAXONOMY
Bacteria
Eubacteria
Coccus

Bacillus Circulans
Bacillus
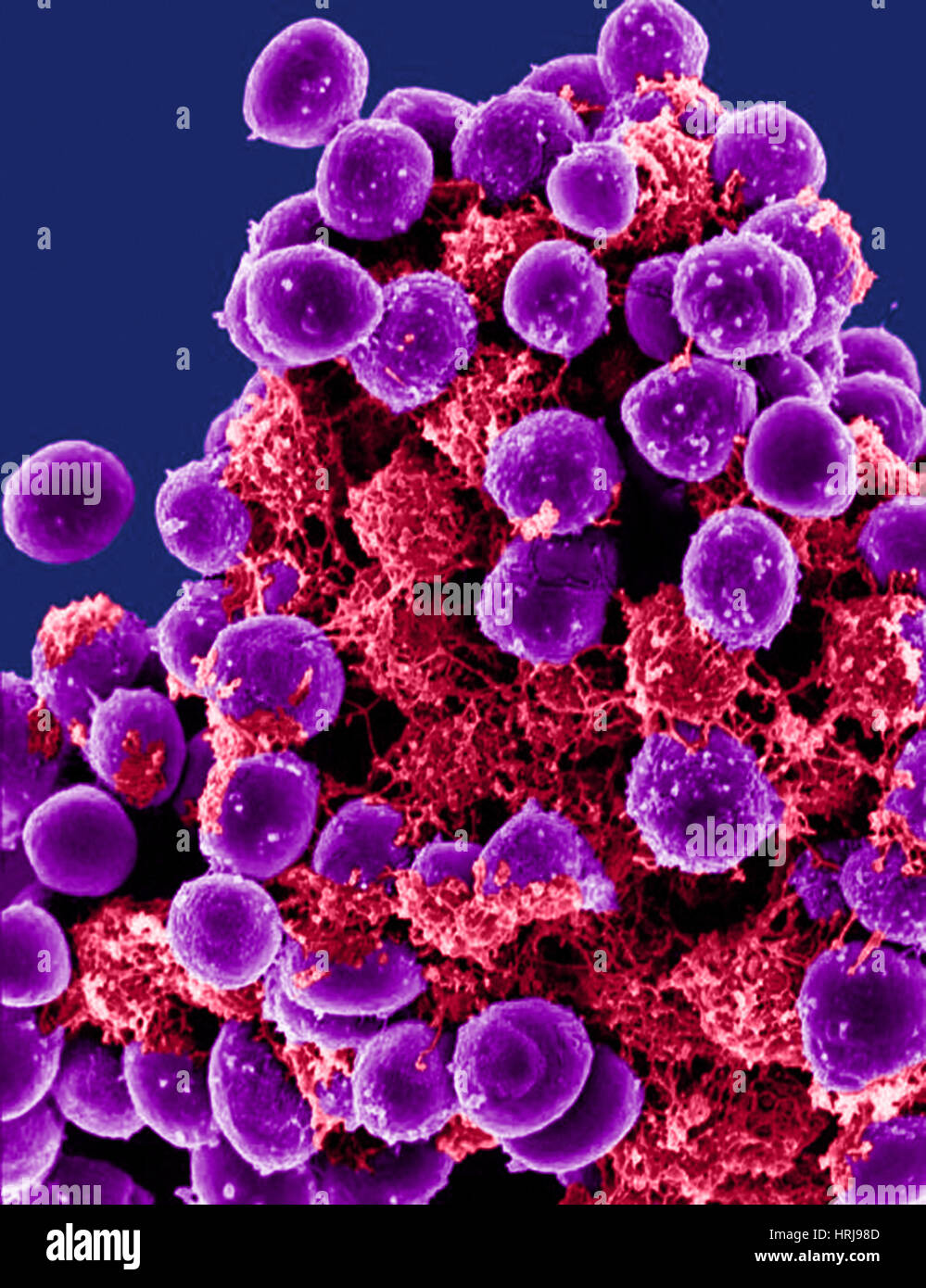
Staphylococcus Epidermidis
Spirillum

Campylobacter Jejuni
Archaebacteria
Halophiles

Thermophiles
Anaerobic Methanogens
Archaea
Protista
Plant-like
Chrysophyta

Prymnesium parvum
Rhodophyta
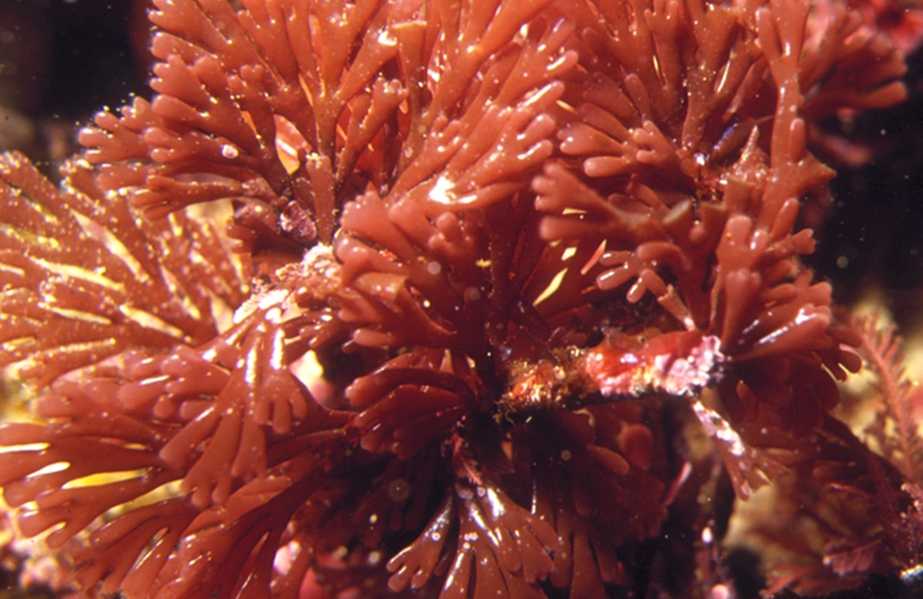

Phymatolithon laevigatum
Euglenophyta

Euglena viridis
Chlorophyta

Eudorina elegans
Pyrrophyta

Cystodinium ineris
Phaeophyta

Phaeophyceae
Fungi-like
acellular slime mold
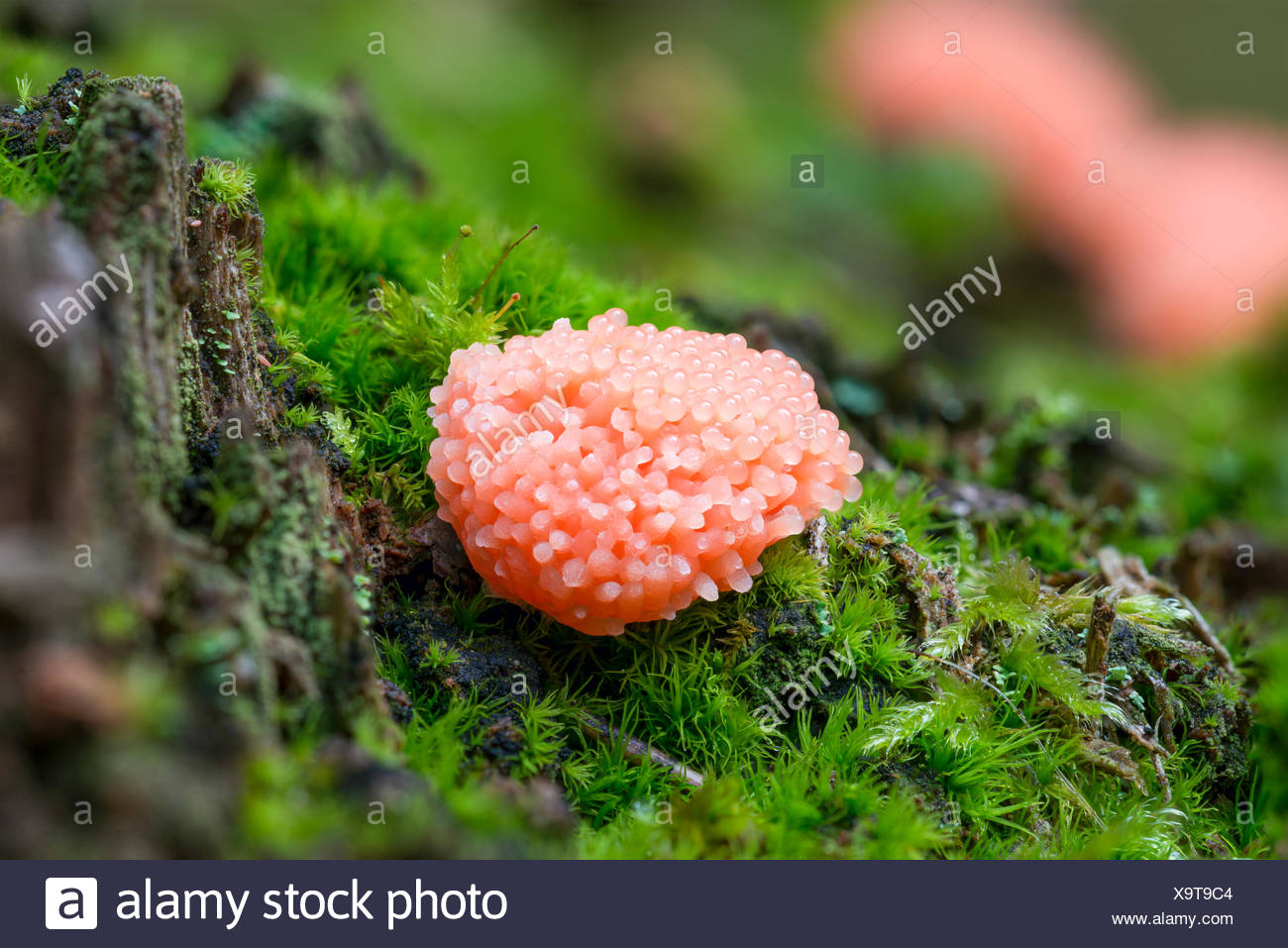

red rasberry slime mold
cellular slime mold
Dictyostelium
Water molds

Pernonosporales
Animal-like
Zooflagellates

Trypansoma Gambiense
Sarcodines

Ameoba Proteus
Ciliates

Paramedcium
Sporozoans
Plasmodium
Eukarya
Fungi
Zygomycota
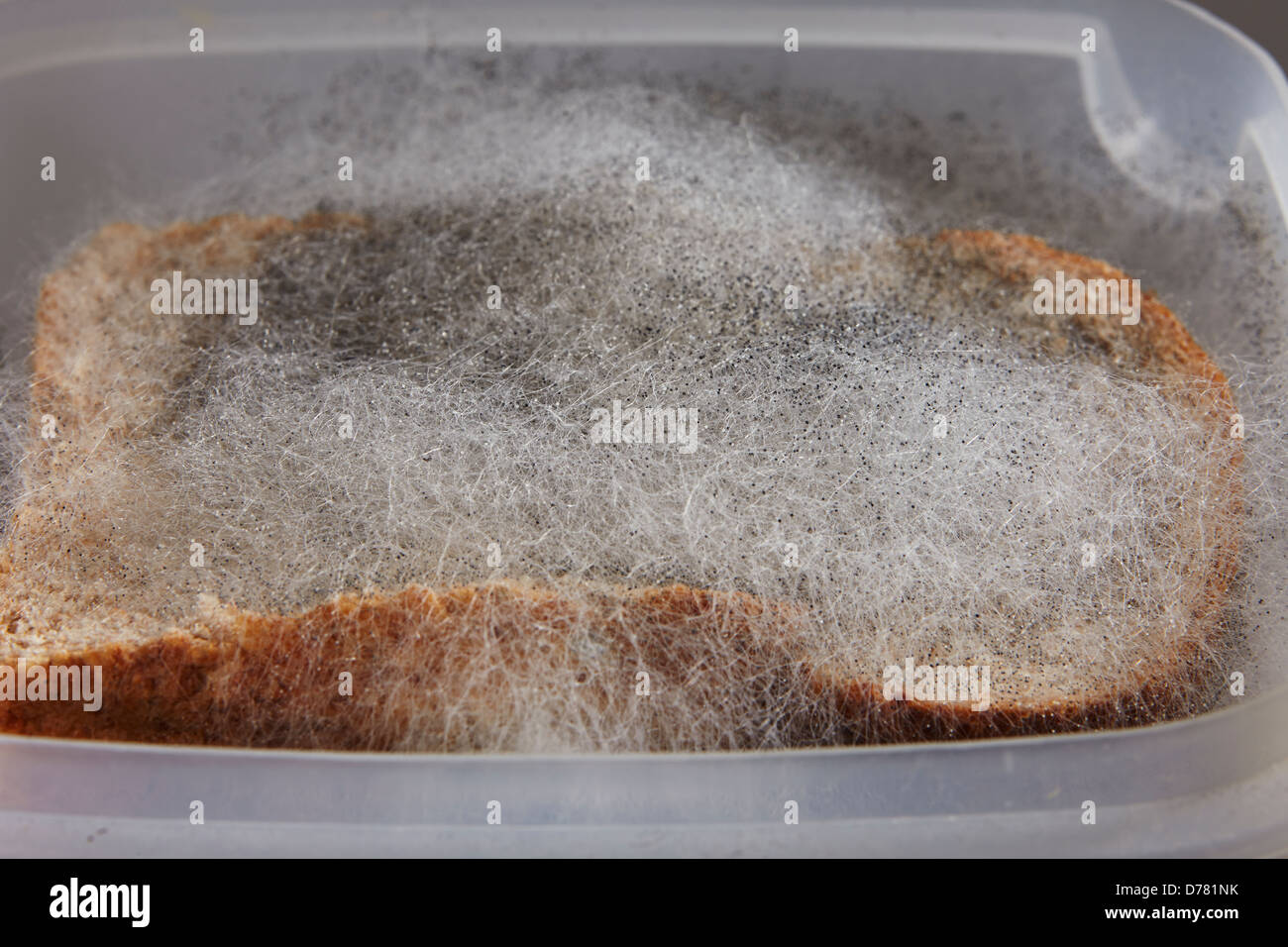

Black bread mold
Ascomycota

Sordariomycetes
Basidiomycota

Agaricales
Deuteromycota

Aspergillus niger
Plants
Bryophytes

Pincushion Moss
Adaptations: non vascular plant,near fresh water, the plants that started off on the water,early stages of plants.
Seedless Vascular
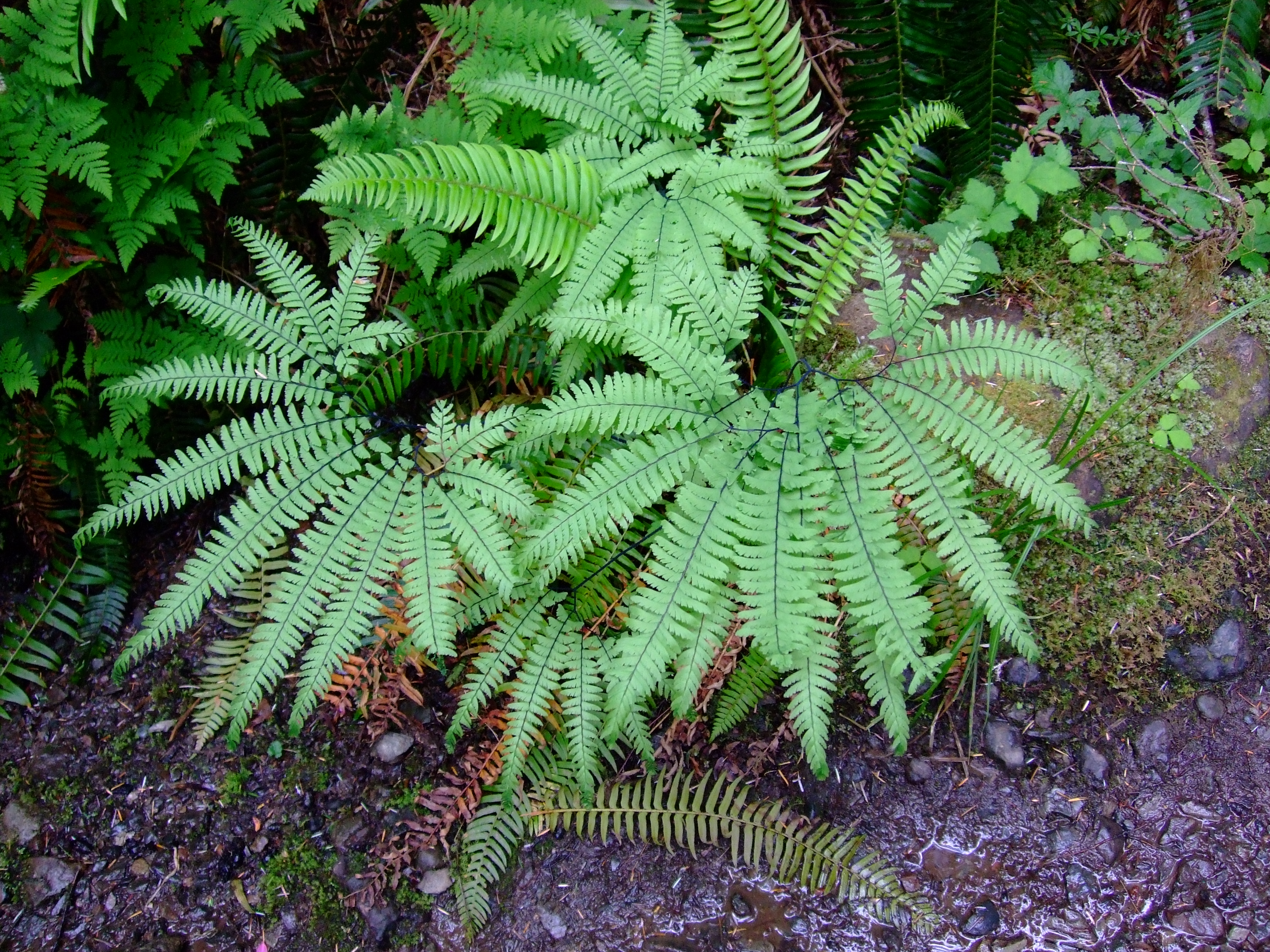

Ferns
Do not produce flowers/seeds, reproduce using haploid unicellular spores, stem which provides structural support and absorb nutrients.
Gymnosperms

Maidenhair Tree
Vascular plant where seeds are stored inside the fruit, autotrophic, photosynthetic organisms that tend to conserve water.roots used for nutrients.
Angiosperms

Magnoliids
Plants that produce flowers and covered seeds, sturdy structure so they they can relieve the sunlight, vascular,
Animals
Porifera
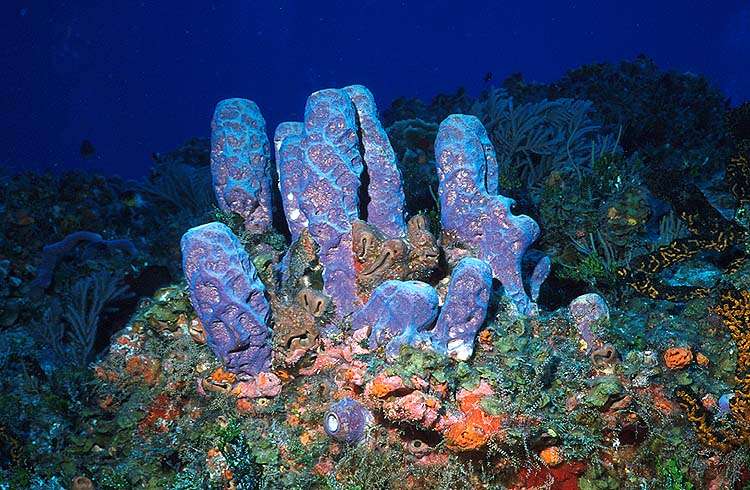

sponges
Nematoda

Roundworms
Cnidaria

Jellyfish
Annelida

Segmented Worms
Platyhelminthes

Flatworms
Mollusca

Squid
Gastropods
Ostreidae
Bivalves
Helix Aspersa
Cephalopods
Octopus
Arthopoda

Crab
Hexapoda

Entognatha

Insecta
Chelicerate

Arachnid

Xiphosura

Eurypterid
Crustacea

Ostracoda

Branchiopoda

Maxillopoda

Malacostraca
Myriapoda

Chillopoda(centipede)

Symphyla(scutigerella causeyae)

Diplopoda

Pauropoda(pauropus huxleyi)
Chordata

Shark
Echinodermata

Starfish
Live in moist aquatic environments
Protists can be unicellular,heterotrophs, autotrophs
- asexual reproduction, most can't move, heterotrophs and autotrophs, cell walls lack peptidoglycan
unicellular prokaryotic cells, single circular chromosome, mostly asexual reproduction, no membrane bound reproduction.
Reproductive strategies: Zygomycota usually produce asexually by reproducing sporangiospores, produce sexually when environmental conditions become unfavorable, to reproduce sexually, 2 opposing mating strains must be fuse or conjugate theregy creating zygospores.
The mainly reproduce by budding and fission, yeasts also engage in sexual reproduction that results in the production of an ascus,placing them in the ascomycota.
Sexual reproduction takes place in the fruiting body,sexual reproduction happens through basidiospores being born on basidia, asexually can be gross similarity to others, by the formation of a distinctive anatomical feature.
They do reproduce asexually and sexual, undergoes sporogenesis like other fungi. When the cell splits apart, and creates a copy of the fungus.
Single celled, Prokaryotic, No nucleus, membrane bound organelles
Protists Reproduce asexually through binary fusion where there is some exchange of DNA
Holozoic, Saprozic
Fungi can be multi cellular or unicellular, fungi are Eukaryotes and heterotrophs
carry out photosynthesis
absorb nutrients
Plants are multicellular, photosynthetic and have a cell wall made of cellulose
simple living organism, asymmetry, no movement(sessile), no mouth,digestion,nervouse system,flagellated cells for water flow.
Digestive system more advanced, two openings are more efficient
Radical symmetry, medusa and polp are the 2 different formd, nerves
Digestive and circulatory system, coelom (real body cavity), body segmentation
Segments were introduced most having a single opening digestive cavity(mouth and anus).
Viceral mass, digestive and circulatory system, foot is used to move,invertebrate
invertebrates,vertebrates, dorsal nerve cord, notochord,paired gill slits,post anal tail, most complex systems
Urochodate
Cephalochordata
Vertebrate
Agnatha(jawless fish)
Representitative Species: Hagfish
Jawed animals

Osteichthyes(bony fishes)

Reptillia

Aves

Amphibia
Chondrichthyes(cartillaginous fishes)
Mammals
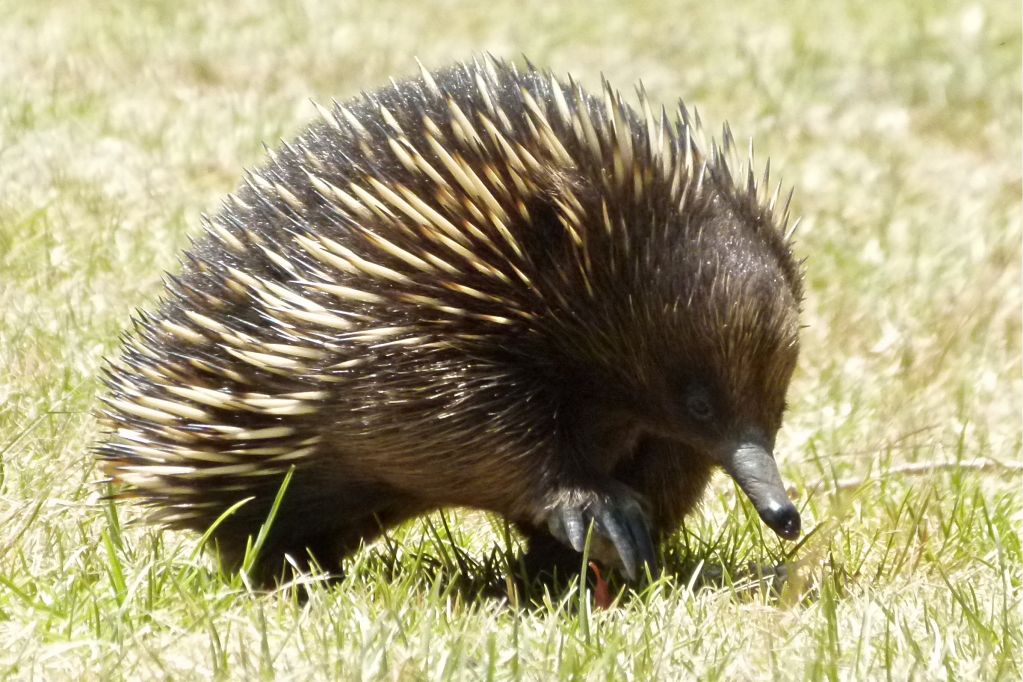

Monotremes

Marsuplals
Placental

Primates

chiroptera
Pholidota