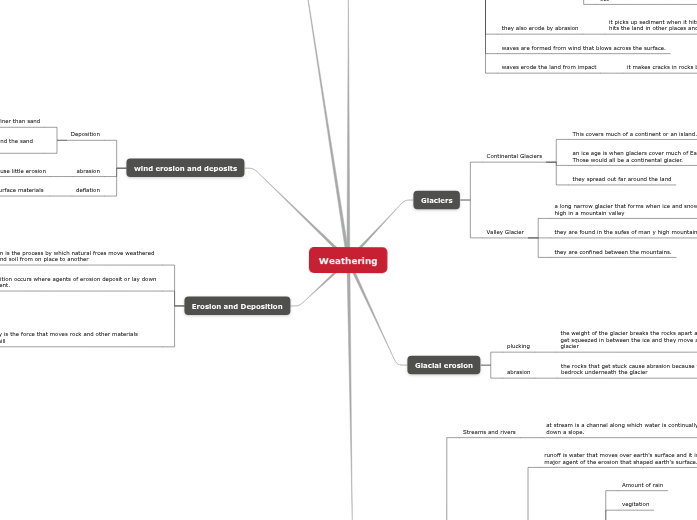
Weathering
Waves and wave erosion
depositional features
sandbar
formed by wave action
spit
formed as longshore drift deposits sand along the shore
Subtopic
beach
waves pile up sand on the shore
waves create land forms
sea stack
left standing when a sea arch collapses.
sea arch
when sea caves on either side join together
sea cave
the waves hollow out the cliff
headland:a part of the shore made of harder rock that sticks out
they also erode by abrasion
it picks up sediment when it hits the beach and the sediment hits the land in other places and erodes it down
waves are formed from wind that blows across the surface.
waves erode the land from impact
it makes cracks in rocks bigger and break it apart.
Glaciers
Continental Glaciers
This covers much of a continent or an island.
an ice age is when glaciers cover much of Eartg's surface. Those would all be a continental glacier.
they spread out far around the land
Valley Glacier
a long narrow glacier that forms when ice and snow build up high in a mountain valley
they are found in the sufes of man y high mountains
they are confined between the mountains.
Glacial erosion
plucking
the weight of the glacier breaks the rocks apart and the rocks get squeezed in between the ice and they move away with the glacier
abrasion
the rocks that get stuck cause abrasion because they grind the bedrock underneath the glacier
water erosion
Streams and rivers
at stream is a channel along which water is continually flowing down a slope.
A large stream is called a river.
runoff and erosion
runoff is water that moves over earth's surface and it is the major agent of the erosion that shaped earth's surface.
Amount of runoff
Amount of rain
vegitation
type of soil
how the land is used
shape of the land
Rills and gullies form whenrunoff travels because of gravity
they are grooves in the land from the water and sediment moving over it.
a floodplain is where a river overflows it covers the extra land around it.
Defonition: the chemichal and physical processes that break down rock at Earth's surface.
types: Chemical and Mechanical
Mechanical
Plant growing
Actions of animals
Abrasion
Freazing and thawing
Release of pressure
Chemichal
Water
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
Living organisms
Acid Rain
Rate of weathering
type of rock
rocks made of more minerals dissolf easier
Permeable rocks are full of little holes that water can seep through
Climate
Average wheather conditions in the area.
both types of erosion occurs faster in a wet climate
wind erosion and deposits
Deposition
loess deposits are made of sediment that is finer than sand
Sand dunes occur when wind strike an obstical and the sand builds up in a pile
abrasion
wind carried sand can polish the rock and cause little erosion
deflation
windremoves surface materials
Erosion and Deposition
Erosion is the process by which natural frces move weathered rock and soil from on place to another
Deposition occurs where agents of erosion deposit or lay down sediment.
sedimentt is the loose peieces of rock or soil moved by erosion
gravity is the force that moves rock and other materials downhill
mass movement
lanslides
rock and soil move quickly down a sleep slope
mudflow
a rapid downhill movement of water, rock aand soil
slump
a mass of rock and soil suddenly slips down a slope in one mass
creep
a very slow downhill movement of rock ad soil