por Nyah Nanton - Robert H Lagerquist Sr PS (1473) 2 anos atrás
405
Charles Spaulding
por Nyah Nanton - Robert H Lagerquist Sr PS (1473) 2 anos atrás
405

Mais informações
In 1986 he published Out of the crisis which documented the thinking and practice that had led to the transformation of the Japanese manufacturing industry.
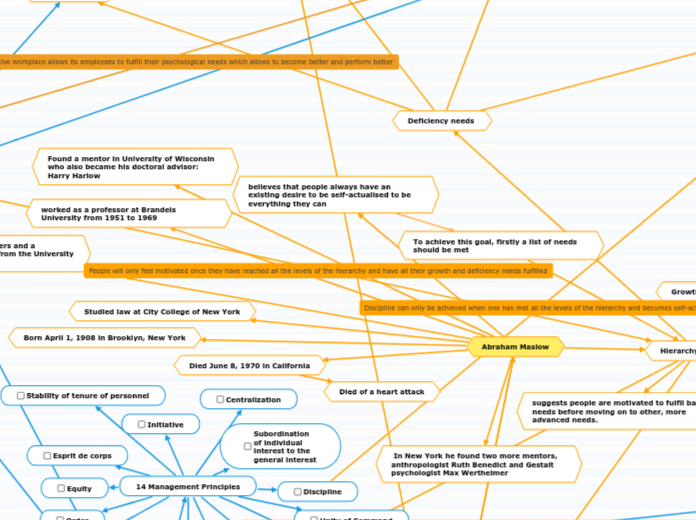
5.Self-actualisation
Peak experiences, according to Abraham Maslow, are associated with happiness. He mentions earlier that self-actualized individuals frequently report feeling happier and more content with their lives in a steady, grounded manner. Maslow claims that self-actualizing individuals have an accurate perception of reality and a sense of wonder, astonishment, and thankfulness for life. Instead of being self-centered, they are problem-centered, centred on how to get better, and not deficiency-centered. They are free thinkers who aren't heavily impacted by pop culture.
Business relation - Give employees the opportunity to think big, to be creative, to have a vision for the future, to reinvent, and provide direct input to senior leadership.
4.Esteem
Abraham Maslow believed that there was a distinct difference between respect or regard and love. He believed that experiencing love and acceptance from families and communities gave rise to the capacity to feel one's own sense of self-worth and individuality. As individuals, we naturally want to succeed or stand out, to be recognised for our special skills and abilities. One has the psychological freedom to be creative and evolve as well as the ability to be more giving to others once they have a certain level of self-esteem and confidence.
Business relation - Empowerment. Public praise. Employee recognition programs. Understanding that each person's job contributes to the ultimate success of the company. Making everyone feel valued and important.
3.Love/Belonging
Humans are social beings, family, friends, and close relationships help many people cope through life's ups and downs. Numerous studies have revealed that those who are most healthy and happy frequently take an active role in their communities.While a lack of social engagement, human connections, and a feeling of community can lead to sadness or loneliness, an excess of love and community can frequently help people get through challenging times.
Business relation - Give everyone the opportunity to be heard. Create a sense of community. Coworkers are part of something bigger than themselves. They have a clear understanding of a value-centered mission.
2.Safety
The second tier of human requirements includes psychological, economic, social, and occupational security. Although physiological demands are more urgent and demanding, losing one's work, family, home, life savings, health insurance, etc. is likely to make one feel incredibly vulnerable and unprotected. A bumper or airbags on a car; while you don't always need them, having them gives you some confidence that you can endure minor bumps and bruises on the road of life. This is how fulfilling the safety needs may be compared.
Business relation - Treat coworkers with respect. Allow them the freedom to take risks and not be harshly criticized or humiliated.
1.Physiological
The physiological needs, such as those for breathing, eating, drinking, sleeping, having sex, and excreting, areprimaryand clearphysiological needs. People become focused with meeting their wants above all else when they are not met. For instance, persons in a conflict zone who are starving may be unaware of danger while looking for food.
Business relation - Safe work environment. Proper lighting. Clean facilities. Airflow. Heat. The correct tools to do the best job.
This goes over the use of technology in the workplace. In Fayol's management principles he talks about innovation and adaptability to change in order to increase productivity. This directly relates to VR/AR as this way we are upgrading the system. Charles Spaulding also relates as he emphasizes innovation and efficiency. With technology we can save much more time and be way more productive and creative with work.
This goes over the use of technology to see the behavior and productivity of employees. This connects to two of Fayol's principles, coordinating and controlling. By installing monitoring it would allow more control and allow every thing to be more organized. Charles Spaulding goes more over integrity, so his principles would cover employee privacy.
This refers to many people leaving their jobs in order to get another job that is better for them. Charles Spaulding described the importance of motivating and developing employees to contribute to organizations. While on the other hand, Henri Fayol's management principles also included motivating and developing employees but also effective communication and decision making to make employees stay.
They both believed in the importance of developing employees skills and abilities and empowering them to contribute to the organizations success.
They both believed that companies have a responsibility to support and invest into their communities.
While Fayol helped build the foundation of modern management theory, Charles Spaulding helped African Americans in the business world. As at the time they were treated bad due to racism/discrimination.
They were both committed to running successful organizations that helped their customers and employees.
Both recognized the importance of communication, decision making, organizational management, efficiency and productivity.
Fayol’s theories are criticized for neglecting the importance of human behavior and motivation. His main focus is more on hierarchy and structure and this may not include interpersonal relationship issues. For example, workers may not be able to contribute their unique ideas and perspectives due to the hierarchy structure.
Some people argue that his theories are outdated and are no longer relevant. His approaches may not be suitable for super flexible and fast-paced environments.
Deming not only developed and made his 14 points of excellence famous, but also brought about a new way of thinking about business management.
how his theories has been applied in real-world business contexts and their life
late 1930s, Deming, a professor of statistics at New York University, developed the so-called “statistical process control,” a philosophy that would revolutionize car production using statistics as a tool to achieve better quality control
His theories were applied at manufacturing companies across Japan, and led to hugely increased productivity, earning him an excellent reputation for reducing expenses and increasing productivity
At Worximity, the 14 points in manufacturing have influenced our Smart Factory analytics that make factories more productive and reliable in the industry.
Toyota and Sony are high-profile examples of companies that applied Deming's 14 points and helped Japan become a world manufacturing leader
It is a theory that says that solving issues as they arise is necessary. With the fundamental objective of achieving customer happiness, a culture of continual improvement must be created and promoted.
Deming’s Theory informs that there is always a solution within the workings of the system
Deming’s Theory is a management philosophy based on systems theory, originally prototyped for use in the automotive industry with Toyota. It turned out that this systems-focused improvement framework translated well to many other industries, including healthcare.
specialization and division of labor
it would help individuals to transform within their organizations, which would, in turn, improve the outcomes in quality improvement efforts
Weber stated that a well-functioning bureaucracy that was designed with the division of labor in mind it would be more orderly and productive than one without it.
Without labor division, people would have to tasks that they are not equipped and know not enough about and do the task wrong becomes unorganized and incorrect.
the both believe that division of work is effective
Authority Hierarchy
Weber believed that Chains of command, and Positional roles or functions in an organization creates power dynamics with those at higher levels giving commands to those lower down in rank its implemented to formalized rules for who gets to give orders to whom within an organization.
impersonality
Weber believed that the relationship between employee and employer should be professional and that would prevent favoritism and promote decision making only based on criteria and solid facts rather then have choices made by the opinions of other employees.
Career Orientation
this means that every employee should have their own special and unique skills that are beneficial to the job assigned them. it also means that since its the employers job to match employees to the right path but also give them a career pathway to help achieve higher positions based on their skill orientation.
formal selection process
All employees are to be selected based on the technical knowledge and ability that they show through formal a examination, training or education that they might have.
its also referred to as Formal Rules and Regulations which means a standard operating procedure that informs workers about how to handle tasks and situations to be fit for the job
standard operating procedures
Weber believed that there should be set rules and polices which are the guidelines about how things should be done so that would keep the mangers in place. as well as the lower level employees
what is a bureaucracy
The term bureaucracy refers to a complex organization that has many layers to their systems and processes. The systems and processes that are put in place effectively make decision-making slow without any bias from other employees. They are designed to maintain uniformity and control within the organization.
The term bureaucracy is often criticized and deemed negative because of the implication that procedures are more important than efficiency. which proves to be problematic in today's society when customers and employees should be at the top of the business pyramid