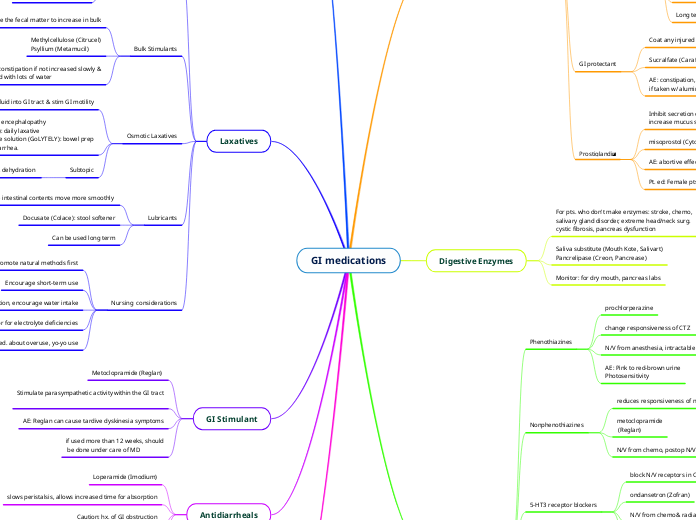
GI medications
Rifaximin
GI bacteria causes ammonia
enceph. pts. can't filter ammonia
Used for hepatic encephalopathy
in conjunction with lactulose (which bind to ammonia)
Works against e. coli to tx. traveler's diarrhea
Box 58.4 on page 1028
Antibiotic that acts locally on the GI tract
Antidiarrheals
AE: constipation
Caution: hx. of GI obstruction
slows peristalsis, allows increased time for absorption
Loperamide (Imodium)
GI Stimulant
if used more than 12 weeks, should
be done under care of MD
AE: Reglan can cause tardive dyskinesia symptoms
Stimulate parasympathetic activity within the GI tract
Metoclopramide (Reglan)
Laxatives
Nursing considerations
Pt. ed. about overuse, yo-yo use
Monitor for electrolyte deficiencies
Monitor for dehydration, encourage water intake
Encourage short-term use
Promote natural methods first
Lubricants
Can be used long term
Docusate (Colace): stool softener
Help the intestinal contents move more smoothly
Osmotic Laxatives
Subtopic
AE: cramping, bloating, dehydration
Lactulose (Constilac): hepatic encephalopathy
Polyethylene glycol (MiraLAX): daily laxative
Polyethylene glycol electrolyte solution (GoLYTELY): bowel prep for procedure. WILL cause diarrhea.
Draw fluid into GI tract & stim GI motility
Bulk Stimulants
AE: constipation if not increased slowly &
used with lots of water
Methylcellulose (Citrucel)
Psyllium (Metamucil)
Cause the fecal matter to increase in bulk
Chemical Stimulants
AE: cathartic dependence
Caution: acute GI disorders, pregnancy
Bisacodyl, senna
Chemically irritate the lining of the GI tract
Natural Methods
Proper diet: high fiber, fresh fruits & veg
Promote healthy gut bacteria
Regular exercise, ambulation
Increase fluid intake
Don’t ignore urges
Antiemetics
Nursing Considerations
Non pharm methods
oral care
Bowel sounds, activity, I&Os
baseline CNS
Assess for dehydration
promethazine (Phenergan)
Risk of extravasation
DO NOT use hand vein
causes drowsiness
H2 antihistamine
Substance P/Neurokinin 1 receptor antagonist
Don't use w/ warfarin PO contraception
Highly emetogenic chemo (cisplatin)
Used in combo w/ dexamethasone
directly block N/V receptors in CNS
5-HT3 receptor blockers
AE: Prolonged QT interval
N/V from chemo& radiation, postop N/V
ondansetron (Zofran)
block N/V receptors in CTZ and locally
Nonphenothiazines
N/V from chemo, postop N/V
metoclopramide
(Reglan)
reduces responsiveness of nerve cells in CTZ
Phenothiazines
AE: Pink to red-brown urine
Photosensitivity
N/V from anesthesia, intractable hiccoughs
change responsiveness of CTZ
prochlorperazine
Digestive Enzymes
Monitor: for dry mouth, pancreas labs
Saliva substitute (Mouth Kote, Salivart)
Pancrelipase (Creon, Pancrease)
For pts. who don't make enzymes: stroke, chemo,
salivary gland disorder, extreme head/neck surg.
cystic fibrosis, pancreas dysfunction
GI reflux and ulcer meds
Prostiglandin
Pt. ed: Female pts of child-bearing yrs: use contraception
AE: abortive effect in pregnancy
misoprostol (Cytotec)
Inhibit secretion of gastrin
increase mucus secretion
GI protectant
AE: constipation, can cause aluminum toxicity
if taken w/ aluminum salts
Sucralfate (Carafate)
Coat any injured area in the stomach
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Long term use should be under care of MD
Long term use: gastric cancer, low Ca, Mag lvls, bone loss, HTN, increase chance of C. diff & PNA
meant for SHORT term tx (4-8 wks.) of GERD, reflux
end in -prazole
Suppress secretion of HCl acid
Antacids
easy to overuse/abuse
AE: electrolyte imbalance, affect absorption of other meds
calcium carbonate (Tums), milk of mag.
Directly interact with acid to neutralized them
Histamine 2 Antagonist
Don's use w/ warfarin, beta blockers, alcohol
AE: heart arrhythmias, low BP
Short-term tx of ulcers & GERD
hypersecretory diseases
end in -tidine
Block release of HCl acid in response to gastrin