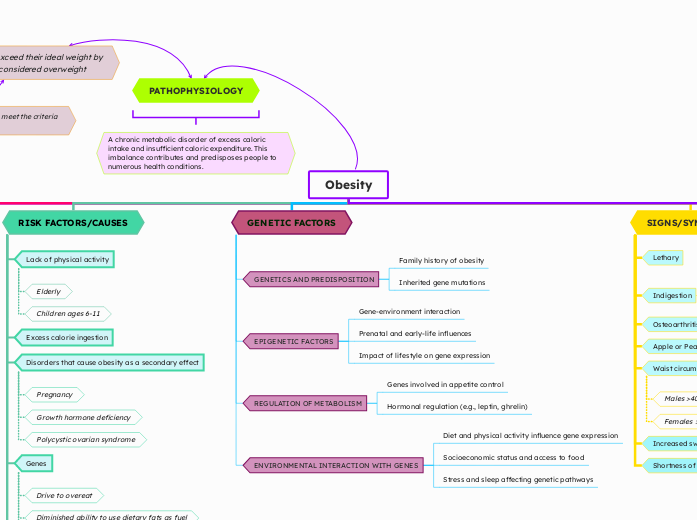
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
A chronic metabolic disorder of excess caloric intake and insufficient caloric expenditure. This imbalance contributes and predisposes people to numerous health conditions.
when that level rises to 30%, they meet the criteria of obesity
Once individuals exceed their ideal weight by 20%, they are considered overweight
185 calories in 30 minutes
Obesity
COMPLICATIONS
High Blood Pressure
Respiratory Issues
Psychological Well-being
Arthritis
At Risk for Diabetes 2
At risk for Heart Disease
PSYCHOLOGICAL IMPACT
Eating disorders related to obesity
Bulimia nervosa
Night eating syndrome (NES)
Binge eating disorder (BED)
Self-esteem issues and depression
Can be very hurtful to someones well being
a big impact on mental health
Social stigma and discrimination
Social isolation
Negative attitudes
SIGNS/SYMPTOMS
Shortness of breath
Increased sweating
Waist circumference
Females >35 inches
Males >40 inches
Apple or Pear shaped excess fat accumulation
Osteoarthritis
Caused by excessive weight on knees and hips.
Indigestion
Caused by GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease)
Lethary
GENETIC FACTORS
ENVIRONMENTAL INTERACTION WITH GENES
Stress and sleep affecting genetic pathways
Socioeconomic status and access to food
Diet and physical activity influence gene expression
REGULATION OF METABOLISM
Hormonal regulation (e.g., leptin, ghrelin)
Genes involved in appetite control
EPIGENETIC FACTORS
Impact of lifestyle on gene expression
Prenatal and early-life influences
Gene-environment interaction
GENETICS AND PREDISPOSITION
Inherited gene mutations
Family history of obesity
RISK FACTORS/CAUSES
Medications
Diabetes medications
Anti-seizures
Antidepressants
Steroids
Non-Smokers
Former smokers replacing the habit with food
Cigarettes act as an appetite stimulant
Eating Disorders
Night Eating Syndrome
Purging Disorders
Binge Eating
Bulimia Nervosa
Anorexia Nervosa
Socioeconomic Status
Poverty
Fewer healthy food choices
Gender
Men burn more calories at rest
Female have less muscle than men
Genes
Enlarged, easily stimulated capacity to store body fat
Diminished ability to use dietary fats as fuel
Drive to overeat
Disorders that cause obesity as a secondary effect
Polycystic ovarian syndrome
Growth hormone deficiency
Pregnancy
Excess calorie ingestion
Lack of physical activity
Children ages 6-11
Elderly
PREVENTION/TREATMENT
Surgery
Bariatric Surgery
Intragastric Balloon Therapy
Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
Gastric Banding
Laparoscopic Roux-en Y Gastric Bypass
Liposuction
Fat reduction in a specific site.
Pharmacology
Phentermine
Rybelsus
Ozempic
Balanced diet
Basal Metabolic Rate
The minimum caloric requirement needed to sustain metabolic processes in a resting state.
ChooseMyPlate.gov
Provide information about healthy and balanced eating.
Activities that cause calorie expenditure
Dance
Cycling
Water aerobics
Walking
Hiking
DIAGNOSIS
Dyslipidemia
High triglycerides
High LDL
Low HDL
Skinfold fat measurement
>30% in females (Triceps, suprailiac, and thigh)
>25% in males (Chest, abdomen, and thigh)
Blood Tests
Blood presure
Glucose
Lipids
Thyroid function
Hormone imbalance
Excess fat accumulation
BMI ≥ 30
Height to weight ratio
wt. in pounds x 703 / ht. in inches / ht. in inches
Exceed ideal body weight by 30%