por Cassidy Ward 5 anos atrás
535
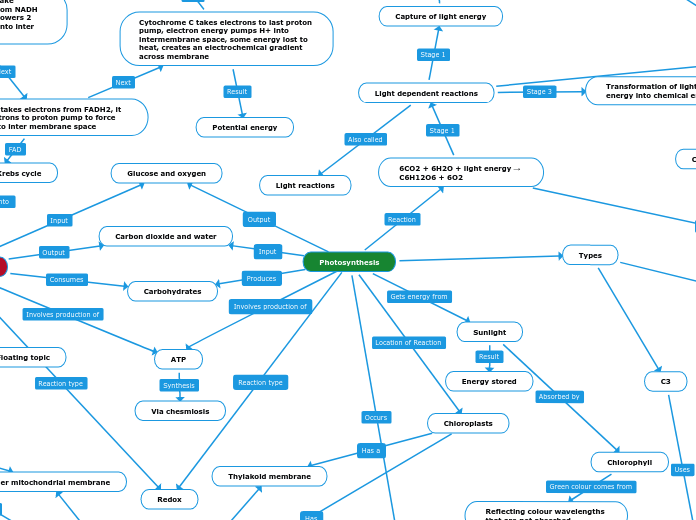
Photosynthesis
por Cassidy Ward 5 anos atrás
535

Mais informações
Ubiquinone takes electrons from FADH2, it carries electrons to proton pump to force more H+ into inter membrane space
Cytochrome C takes electrons to last proton pump, electron energy pumps H+ into intermembrane space, some energy lost to heat, creates an electrochemical gradient across membrane
Electrons have low energy from pumping H+, water is created when oxygen accepts these electrons and binds to 2H+
H+ channel proteins in membrane let H+ come into matrix creating kinetic energy with their movement creating ATP
Potential energy
Returns to Krebs cycle
FADH2
Reenters Krebs cycle
4 CO2, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP
Citrate
Isocitrate
A-ketoglutarate
Succinyl-CoA
Succinate
Fumarate
Malate
Oxaloacetate
Product
Reactant
NAD+ oxidizes each 3-carbon pyruvate molecule, addition of two electrons and protons creates NADH and H+, leftover products create acetic acid
acetyl-CoA is created when coenzyme A bonds to acetic acid
6-carbon glucose molecule into 2 3-carbon molecules (G3P using 2 ATP after fourth reaction
Production of 2 NASH and 4 ATP + both G3P converted into 2 2-carbon pyruvate molecules
Do better in hot, dry climates
Photorespiration
Completing C4 pathway at night time, Calvin cycle during day time
Very efficient in hot, dry weather
Temporal seperation
Does not do well in hot, dry area, less efficient when higher rate of photorespiration is required
Regeneration
Cycle to repeat itself
PGAP goes through a reduction reaction powered by NADPH from previous reactions to make G3P
One G3P leaves, 5 stay to power cycle again
Produces carbohydrates
Glucose and Fructose
Sucrose and starch
NADH
NADPH created when NADP reductase uses electron energy to attach H+ to NADP+
ATP
Chesmiosmosis from proton motive force created by concentration difference between storm and lumen side
ATP synthase
During photolysis, photosystem 680 removes electrons from H2O to release H+ ions
Chesmiosmotic gradient created by pumping protons into lumen of thylakoids
Photosystem II transfers electrons to photosystem I, along a pathway from plasoquinone to 6-f complex to pastocynanin
Electron transport chain
Ferrodoxin transfers electrons to NADP reductase
Diffuses out of chloroplast
Electrons in chlorophyll molecules attached to thylakoid membrane absorb a photon of light energy
Electron charged and moves from chlorophyll a to another pigment, electron passed along Antenna system to reaction centre
Primary electron acceptor captures electron, oxidizing reaction centre
Contains two arrangements of pigments and proteins
Photosystem 700, used second
Photosystem 680, used first