por Alsaadi Bahaa Al Deen 3 anos atrás
1164
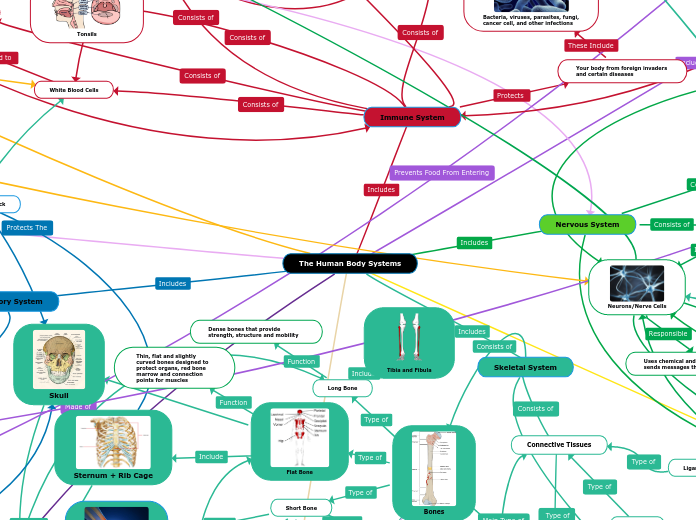
The Human Body Systems
por Alsaadi Bahaa Al Deen 3 anos atrás
1164

Mais informações
Electric shock
Reestablishes an effective heart beat
Makes the heart start beating
Clears blood clots
Space for blood to flow
Types of proteins which attack antigens and remove them from the body
Antigens
Toxins or foreign substances which are killed by Antibodies
Is cut into small holes
Are placed inside
Surgery without cutting too much skin
Is let in your stomach through the esophagus
Surgury is used
82% Success Rate
A Portion of the stomach around the Esophogus
Acid Reflux
Enzymes
Bile
Small Intestines
Nutrients
Carbohydrates and fats
Protiens
Vitamins/Minerals
Further digest food
Large Intestines
The remaining Food (without nutrients) into feces
The food using enzymes and gastric acid
Sensory Receptors
Involuntary Swallowing Reflex
Epiglottis
Choking
The Uvula
Saliva
Nasopharynx
Air Flow into your lungs
Fauces
A Passageway
The Throat
Esophogael Sphincter
Lower Esophogael Sphincter
Muscular valve
When there is not food entering the esophogus
When food is passing through
Upper Esophogeal Sphincter
Tongue
Food into the pharynx/esophogus
Yellow Bone Marrow
Fat, cartilage, and bone cells
Red Bone Marrow
Stem Cells
Specific instructions
The potential to become all other types of cells
Renew themselves over a period of time
First Cells in your cell linage
Skull
Sternum + Rib Cage
Thin, flat and slightly curved bones designed to protect organs, red bone marrow and connection points for muscles
Patella
Short bones, usually containing spongy material, help provide stability and small movement adjustments to wrists and ankle joints
Tarsal Bones
Carpal Bones
Dense bones that provide strength, structure and mobility
Tibia and Fibula
Helps keep diaphragm and lungs in place, while also helping the diaphragm to contract and expand
When diaphragm contracts, it creates a vacuum which sucks air from the outside into your respiratory system, and when it stretches it pushes air back out of your respiratory system
Interneurons
Relay interneurons
Local interneurons
Uses chemical and electrical signals to sends messages throughout the body
Paralysis
There is no cure to paralysis since the spinal cord cannot repair it self, and usually an amputation is needed
Amputation
Amputation is the removal of a body part and is usually replaced by prosthetic
Damage to spinal cord from an injury, event or birth defect called spina bifida
Loss of ability to move some or all of your body
connects everything in the nervous system
Four Interconnected Lobes
Controlling Emotions, Memory, Touch, Motor Skills, Hunger, Breathing, and the other senses in our body. The Brain controls every muscle, bone, organs, and body system.
Parasympathetic nervous system
The top and bottom of the spinal cord
Responsible for conserving energy to complete involuntary actions and drives the "rest and digest" conditions in quiet situations
Sympathetic nervous system
The center of the spinal cord
Responsible for increasing heart rate, body temperature, blood pressure and creating sweat in stressful situations driving the "fight or flight" conditions
Regulates involuntary actions such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, digestion, body temperature and sexual arousal
Motor neurons
Moves information from the brain and spinal cord to the fibers and muscles in the body
Sensory neurons
moves information from the body to the Central nervous system
connects the central nervous system to the muscles throughout the body
Bones
The strengthining of Bones
Joints
Proper Muscle Function
Electromagnetic signals that are produced by the atomic nuclei inside teh molecules of a muscle tissue
Scan Tissues
Muscle Diseases
The Heart struggling to work
Heart Failure
Dysfunction of muscle fibers
Struggle and stiffness of muscles
Antagonistic Pairs
Quadriceps and Hamstrings
Biceps and Triceps
Muscle Relaxes
Antagonist
Muscle Contracts
Agonist Muscle
Stripped Appearance
Under our control and are involuntary actions
Walls of Vessels
Walls of Internal Organs
Are organism which lives inside a host organisms (Human Body) Recieve energy by feeding on the internal organs of a host
Can live outside of a host (Air, Surfaces) Thrive and stay alive by affecting other cells, making copies of its self.
Found almost everywhere in the world, there are good types and dangerous types of bacteria
Pheromones are a type of chemical which hair creates in other animals of the same species which helps in mate finding and looking attractive
Sebum, also known as natural oils, protects, moisturizes and coats your skin
Cryosurgery
Is Frozen
Liquid Nitrogen
Skin is cut off
Cancer from Spreading
Overexposure to sunlight, usually because of a low amount of body oil, which causes the UV rays from the sun to damage to DNA in the skin, causing abnormal cells to grow. These cells can divide in a disorganized manner which creates a mass of cancer cells
Small smooth waxy bumps on the face, ears, and neck. Flat pink/red or brown colored lesion on arms and/or legs. Areas on the skin look like scars. Sores that look crusty and bleed often
Protects the body from harm such as UV radiation, bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites and chemicals.
Melanocytes
Creates melanin which is a group of pigments which provide us with our skin colour
Basale
Deepest layer of the epidermis, creates keratinocytes which when exposed to sunlight helps create protein, lipids and vitamin D
Granulosum
Uses a chemical called glycolipids to glue skin cells together
Lucidum
Only present in thicker layers of skin such as palms and soles
Corneum
The topmost layer of skin, thickness varies and it plays the first line of defense against other organisms
Located on the bottom and connects the skin to the bones and muscles
Macrophages
Macrophages are a type of white cells which fight off unknown organisims such as fungai, viruses and bacteria when the tissue is injured
Adipose
Commonly known as body fat and is used to store excess nutrients as fat and is also used as a type of shield
Connective tissues
Cells, fibers and gel like substance
Supports organ structure and helps connect other tissues and organs in the body
Made from fibroblast cells as they help maintain the structural framework of tissues
Protects body, supports epidermis, provides elasticity to the skin, a sense of touch since the nerves are located in the dermis, and heat
Hair folicles
Vitamin A, Vitamin B, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, iron, zinc and proteins
When the hair is unable to push through the skin, usually due to Fungai or infections, a red or white pimple grows around the hair follicles
Tunnel shaped structure in the dermis and epidermis which grows hair in the bottom of it, this hair then pushes up through the skin
Telogen, also known as the resting phase, is when the old hair falls out and the new hair begins to grow from the same follicle, this takes around 2-4 months. These phases repeat constantly
Catagen, also known as the transitional phase, is when the growth slows down and the follicles shrinks, usually lasts 2-4 months
Anagen, also known as the growth phase, is when the hair starts growing from the root and usually takes 3-7 years
Oil and sweat glands
everywhere in the body, mostly found in the forehead, arm pits and palms
Disposes water with salt to lower body temperature, as the water in the sweat evaporates it cools the body down since it takes it heat
Tubes that propel urine from the kidneys into the bladder, usually 20-30cm long and 4 mm in diameter
Percutaneous Lithotripsy
Drinking lots of water, pain relievers and medical therapy for small sized stones
Severe pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills and blood in your urine
When someone drinks too little or too much water, exercise too little or too much, obesity, weight loss surgery and eating foods with lots of sodium or sugar. On rare occasions it can be caused by a malfunction in the thyroid gland
When the many pathways in the kidney (mainly uterus) get blocked by clumps of sodium or salt causing the kidney to malfunction
Nephron
Simple two step process where the glomerulus filters your blood, and the tubule returns the needed substances back into the blood while also removing the waste creating urine
Capsule
Protects the kidney from the outside and helps support the kidneys mass
Pyramids
Carries urine from the nephron to the calyx before it reaches the baldder
Renal cortex
Protects the inner structure of the kidney, mainly the pyramids and nephron
Calyx
Collects fluids from the nephron before it passes through the bladder, extra fluids become urine in here as well
Posterior pituitary gland (back side)
Cushing disease
Tumor
Pituitary radiotherapy
Radiation from an external device
The DNA
The human skin and bone
Severe fatigue, muscle weakness, depression, anxiety, loss of emotional control, high blood pressure, headaches and infections
Noncancerous tumor on the adrenal which gets worse without proper treatment
Occurs when your body produces too much cortisol
Growth hormones
Adrenal (produces adrenaline) and Cortex (produces cortisol)
Anterior pituitary gland (front side)
Signals to the mammary glands to produce milk
During birth or labor
Kidney function
Lateral
Movements, pressure, vibrations and spatial awareness
Medial
Decision making
Pervinitluclar
Aging of the human body
Ventromedial
Controls fear, thermoregulation and sexual activity
Mammillary
Controls memory, mainly recollective memory which begains with hippocampus located in the brain
Tuberal
Controls the feeding impulses
Supraoptic
Create and secrete the peptide hormone vasopressin, or antidiuretic hormone, responsible for controlling the body's blood pressure, sodium regulation and kidney function
Females
Responsible for creating egg cells called ova occytes
Produce adrenaline, aldosterone and cortisol
Stress hormone which increases sugars in the bloodstream and enhances your brains use of glucose and substances that repair tissues
Steroid that plays the main role in regulating the slat and water in the body which effects the blood pressure
Triggers the bodies fight or flight response and causes the air passages to dilate and provide more nutrients and oxygen to the bodies muscles
Plays a huge role in the development of the human body by making sure the thyroid hormones are steady in the bloodstream
Only found in males
Creates sperm cells and a hormone called testosterone responsible for maturity and puberty
Left Side
Right Side
Systemic Arteries
Blood from the Left Ventricle to the rest of the body
Pulmonary Arteries
Blood from the Right Ventricle to the lungs so it can be oxygenated
Oxegenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body
Systemic Veins
Low Oxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium
Pulmonary Veins
Blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart
Unoxygenated blood from the body to the heart
Sinusoid Capillaries
Allow for exchange of larger molecules, even cells since they are a type of capillary vessels with a wider diameter, found in endocrine glands, bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen and liver
Fenestrated capillaries
Blood vessels with tiny pores, or holes, which allow larger molecules and proteins to move from your blood into organs, usually found in kidneys, intestines and pancreas
Continuous capillaries
The smallest blood vessels, responsible for connecting your arteries to your veins and support your brain, endocrine system, kidneys, lungs and the small intestines