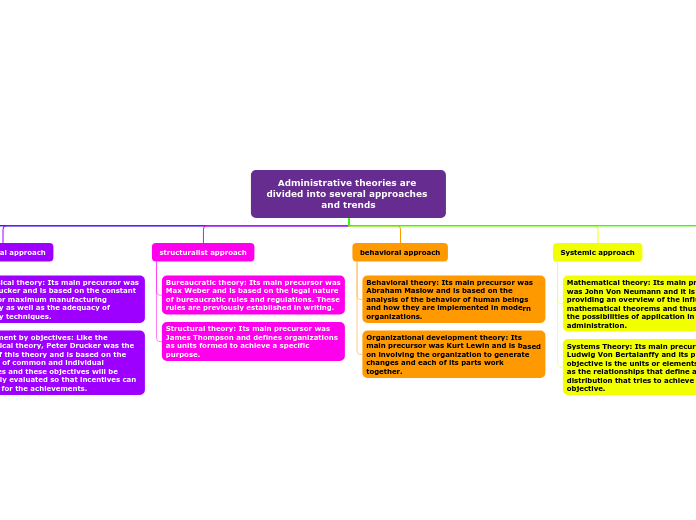
Administrative theories are divided into several approaches and trends
classic approach
Scientific theory: Its main precursor was Frederick Taylor and is based on applying procedures according to scientific methods.
Classical theory: Its main precursor was Henry Fayol and is based on establishing a predominance of common sense and maintaining competent guidance.
humanistic approach
Theory of human relations: Its main precursor was Elton Mayo and it seeks to obtain good management of the human team and thus obtain autonomy and democracy as well as a good relationship between employees, making relationships of trust and discretion.
neoclassical approach
Neoclassical theory: Its main precursor was Peter Drucker and is based on the constant search for maximum manufacturing efficiency as well as the adequacy of efficiency techniques.
Management by objectives: Like the neoclassical theory, Peter Drucker was the author of this theory and is based on the proposal of common and individual objectives and these objectives will be constantly evaluated so that incentives can be given for the achievements.
structuralist approach
Bureaucratic theory: Its main precursor was Max Weber and is based on the legal nature of bureaucratic rules and regulations. These rules are previously established in writing.
Structural theory: Its main precursor was James Thompson and defines organizations as units formed to achieve a specific purpose.
behavioral approach
Behavioral theory: Its main precursor was Abraham Maslow and is based on the analysis of the behavior of human beings and how they are implemented in modern organizations.
Organizational development theory: Its main precursor was Kurt Lewin and is based on involving the organization to generate changes and each of its parts work together.
Systemic approach
Mathematical theory: Its main precursor was John Von Neumann and it is based on providing an overview of the influence of mathematical theorems and thus showing the possibilities of application in administration.
Systems Theory: Its main precursor was Ludwig Von Bertalanffy and its purpose or objective is the units or elements, as well as the relationships that define a distribution that tries to achieve an objective.
situational approach
Situational theory: Its main precursor was Paul Hersey and it is based on the fact that the managerial style reflects a high concern and theories and low interest in people and relationships. This style of senior management involves giving explicit directions about how and when tasks should be performed. In this phase, it is most appropriate for the leader to observe many of the behaviors related to the tasks.
Organizational trends
Continuous improvement: It is the one that aims to improve processes or services of organizations.
Total quality: It is the one that consists of improving products and services of the company taking into account the demands of the client.
Benchmarking: It is the next to investigate or know factors so that its competition is much better using new plans, differentiating skills with other organizations in order to match or surpass the competition.
Reengineering: It is the method in which the basic methods of an organization are analyzed and modified.
Project management: It is the discipline of planning, organization, motivation, and control of resources in order to achieve one or more objectives.
Outsourcing: It consists of mobilizing resources to an external company through a contract. In this way, the subcontracted company carries out activities on behalf of the first.