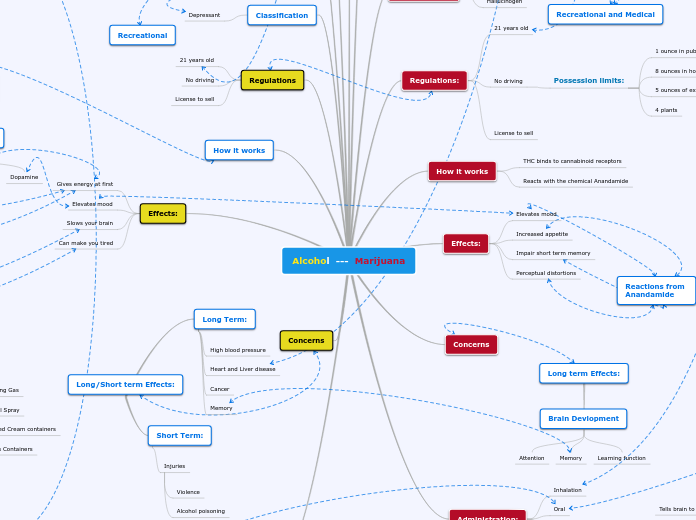
Alcohol --- Marijuana
Common forms:
Leaf, Edibles, and Extract
Usage:
Eating
Joint
Blunt
Pipe/Bong
Classification:
Depressant
Hallucinogen
Regulations:
21 years old
No driving
Possession limits:
1 ounce in public
8 ounces in home
5 ounces of extract
4 plants
License to sell
How it works
THC binds to cannabinoid receptors
Reacts with the chemical Anandamide
Effects:
Elevates mood
Increased appetite
Impair short term memory
Perceptual distortions
Concerns
Administration:
Inhalation
Oral
Sublingual
Topical
Common forms:
Liquid
Usage:
Shots
Beer
Wine
Mixed drinks
Classification
Depressant
Regulations
21 years old
No driving
License to sell
How it works
Effects:
Gives energy at first
Elevates mood
Slows your brain
Can make you tired
Concerns
Administration:
Drinking
Oral
Injection
Recreational and Medical
Caffeine
Common Forms
Coffee, Chocolate, Tea, and Energy Drinks
How its used
Drinking
Caffeine Pills
Creams (redness)
Classification: Stimulant
Increases Alterness
Increased Heart Rate
Increased Blood Pressure
How it Works
Stimulates Central Nervous System
Blocks Adenosine
Effects
Feel awake or more alert
Diuretic
Increased blood pressure
Concerns
Roots of Administration
Oral
Gum
Mouth Sprays
Mouth Rinsing
Regulation
Generally Unregulated
Cannot sell in bulk
Must be listed on ingredients
Recreational
Ethanol binds to
GABA and MDMA
Releases Chemicals:
Cortisol
Norepinephrine
Adrenaline
Dopamine
Reactions from Anandamide
Long term Effects:
Brain Devlopment
Attention
Memory
Learning function
Long/Short term Effects:
Long Term:
High blood pressure
Heart and Liver disease
Cancer
Memory
Short Term:
Injuries
Violence
Alcohol poisoning
Long Term/Short Term
Long Term
Weakness/Fatigue
Difficulty Sleeping
Irregular Heart Rate
Short Term
Restlessness
Anxiety
Higher Body Temperature
Tobacco
Effects
Increases mood
Distracts brain from unpleasant feelings
Shortness of breath
Common Forms
Cigarettes, Cigars, Chew, Electronic Pens
Classification: Stimulant
Increases alertness
Increased Heart rate
Increased Blood Pressure
Subtopic
How It Works
Absorbed into blood
Immediately Stimulates Adrenal glands
Stimulates central nervous system
Increase in blood pressure
Roots of Administration
Smoking
Oral
Rectal
Concerns
How its used
Smoked
Chewed
Sniffed
Regulation
Must be 21
Requires health warning
No flavored cigarettes
Short/Long term
Short Term:
Bad Breath
Coughing
Reduction in smell and taste
Long Term:
Dependence
Cardio disease
Respritory issues
Cancer
Meth
How its Used:
Smoking
Snorting
Swallowing Pills
Classification:
Stimulant
Releases high amounts of Dopamine
Affects central Nervous system
Regulation
Schedule 2 Stimulant
Prescription only
Illegal to:
Possess
Sell
Buy
Effects:
Increase in energy
Feelings of Invlnerability
Psychoactive Effects
Roots of Admin
Inhale
Orally
Snorting
Common Forms
Chunks
Powder
Crystal Shards
Liquid
How It works:
Massive release of:
Norepinephrine
Dopamine
Powerful Euphoric effects
Concerns
Medical Use
Schedule 2 Stimulant
Must be prescribed
Short/Long Term
Short
Increased Wakefulness
Faster Breathing
Rapid and Irregular Heart Beat
Long
Extreme Weight Loss
Addiction
Dental Problems
Death
Nitrous Oxide
Common forms
Laughing Gas
Aerosol Spray
Whipped Cream containers
Nitrous Containers
Classification:
Inhalant
Psychoactive Effects
Mind Altering Effects
Regulation:
Not regulated by Federal Gov.
FDA has no Regulations
Roots Of Admin:
Inhalation
How its Used:
Inhaled
Concerns
Effects
Euphoria
Numbness of body
Sedation
Sudden Death
Varied Effects
Weight
Tolerance
Amount Taken
Short/Long Term
Short:
Shivering
Anesthesia
Vomiting
Fatigue
Long:
Damage to Central Nervous System
Damage to Blood Cells
Liver and Kidney Problems
Opioids
Common Forms:
How it Works:
Attaches to Opioid receivers
Blocks pain
Tells brain to be calm and happy
Effects:
Concerns
Addiction
Legal to Illegal Use
Death
How its Used
Medicinal for pain relief
Hydrocodone
Oxymorphine
Illegally
Injection
Snort
Pills
Regulation:
Illegal for Public use
Schedule 1 Drugs
Class A Felony
Roots of Administration:
Injection
Oral
Transdermal
Natural Opioids:
Occurs in Plants
Morphine
Codeine
Thebaine
Semi-Synthetic
Altered in Labs
Hydromorphine
Hydrocodone
Oxycodone
Fully Synthetic
Completely Man made
Fentanyl
Pethidire
Methadone
Classification:
Short/Long Term
Short Term:
Clam/Sleepiness
Confusion
Nausea/Vomiting
Long Term:
Heart Infection
Lung Infection
Muscle Pain
Psychedelics
How its Used:
New Medial research
Shows positive results
PSTD
Depression
Addiction
Eat/Smoke/Oral Absorption
Common Forms:
LSD
Psilocybin
Peyote
DMT
Regulation
Current fight for loosening Regulation
Schedule 1
"No medical use'
Illegal
Concerns:
Manic Deppression
Extended Sleep loss
Roots of Admistration:
Tablets or pills
Liquid
Snorting
Injection
Classification:
Hallucinogen
Sensations and images that are not real.
Dissociative drugs
Some can make you feel out of control
How it Works
Perception altering affects
Acts on neural circuits in brain
Prefrontal cortex is most affected
Effects:
Short Term
Seeing images
Seeing Images
Unreal sensations
Long Term:
Visual disturbances
Disorganized Thinking
Paranoia
Mood disturbances