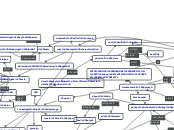
ACID ROCK DRAINAGE PREVENTION BY IMPROVING PACKED BED STABILITY
Chemical Approach
coat sulfidic rocks
apply synthetic coatings
rock sample characterisation
determine sulfur content
determine ARD producing potential
ABA tests
Biokinetic tests
microbes
surface area
pH
[Fe2+]/[Fe3+]
[SO4^2-]
Geotechnical Approach
Physical
Investigate rock mineralogy
PSD
Vary waste rock to fine waste ratio (w/w)
waste rock shape
porosity
Mechanical
packed structural bed strength
packed bed compressibility behaviour
compressive load
compressive extension
Develop Packing Protocols
Analyse packing methods
sample loading approach
consolidated partilcle settlement
rodding
shoveling
jigging
non-consolidated packing settlement
Aspect ratio
bed diameter
bed height
solid material volume
Carry out column leach tests
Fe/Ferrous Ion concentration
permeant flow rate
pH
Sulphate concentration
yield stress
sample rheology
Slump
spread
slump height