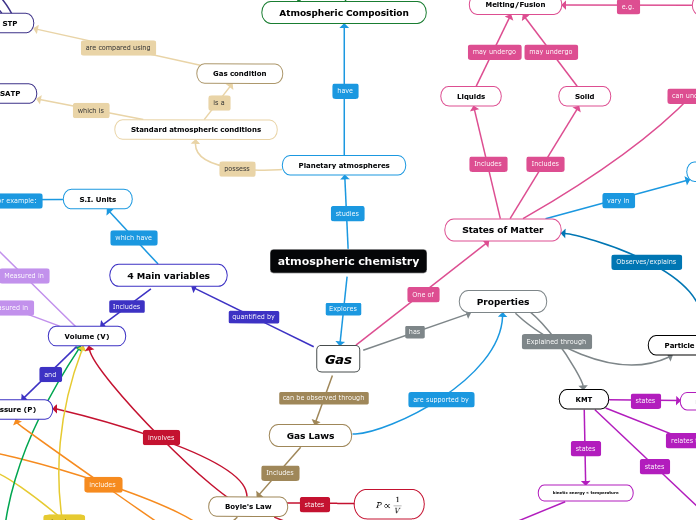
atmospheric chemistry
Gas
Gas Laws
Properties
4 Main variables
Volume (V)
L
Pa
K
S.I. Units
°C
number of particles (n)
Absolute Temperature
States of Matter
KMT
Particle theory
Solid
Liquids
state changes
Melting/Fusion
Temperature (T)
Pressure (P)
particles
Impacts from particles on surfaces create pressure
Boyle's Law
Gay-Lussac's law
Charles's Law
Gas is highly condensable, no fixed shape
-273.13
particles are small, spehrical entities
Combined Gas Law
Ideal Gas Law
Molar Constant (R)
mol
molar mass
g/mol
mole fraction
ratio of moles of one substance vs. total substances in gas mixture
partial pressure