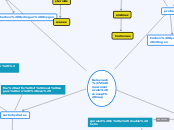
Belaynesh's macromolecule concept map
carbohydrates
monosaccharides
one monomer sugar( glutenous)
Disaccharides
two monomers (sucrose)
Polysaccharides
large polymers(starch)
Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen (always in a 1.2.1 ratio)
sugars
starches
cellulose
glycogen
quick energy
energy storage
structure
the suffix of most sugars are (ose)
lipids
triglycerides
Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen
energy storage
cushions organs
isolates body
fats
oils
phospholipids
steroids
waxes
non polar
hydrophobic (does not like water)
long hydrocarbon chains
glycerol+ fatty acids
nucleic acids
Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen nitrogen phosphorous
store hereditary information
DNA
RNA
single nucleotide chain
spiraled in a double helix
double helix shape
nucleotide
a base, a pentose sugar (ribose/RNA| deoxyribose/ DNA ), and a phosphate group
protiens
20 amino acids (building block)
amino acids are chained into a polymer
chained by peptide bonds
they can be electrically charged or not, they can be polar or non polar.
3D
Primary structure: a series of amino acids.
Secondary structure: chains, folds and coils alpha helix and pleated sheets
Tertiary structure: the weaving of the alpha and beta sheets
Quaternary structure: when more than one chain bonds together.
proteins only work if they have the right shape.
temperature and acidity can denature or unfold the protein
Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen
Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen nitrogen
hormones
movment
immune system
enzimez
transport
mussels
fingernails
skin
hair
enzimez
hormones