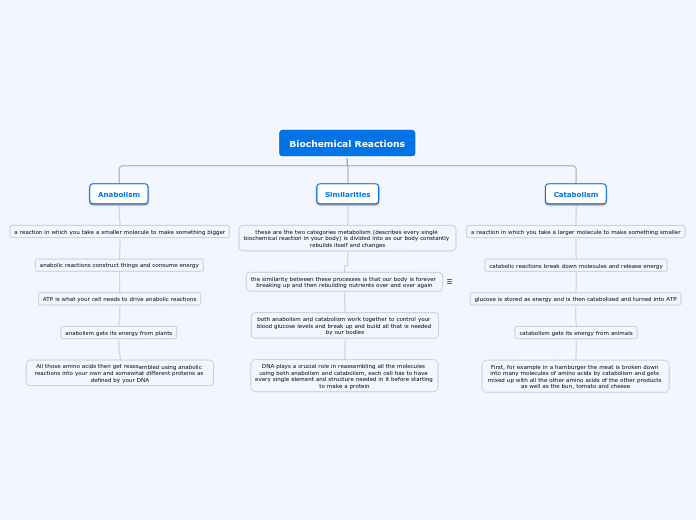
Biochemical Reactions
Anabolism
a reaction in which you take a smaller molecule to make something bigger
anabolic reactions construct things and consume energy
ATP is what your cell needs to drive anabolic reactions
anabolism gets its energy from plants
All those amino acids then get reassembled using anabolic reactions into your own and somewhat different proteins as defined by your DNA
Similarities
these are the two categories metabolism (describes every single biochemical reaction in your body) is divided into as our body constantly rebuilds itself and changes
the similarity between these processes is that our body is forever breaking up and then rebuilding nutrients over and over again
both anabolism and catabolism work together to control your blood glucose levels and break up and build all that is needed by our bodies
DNA plays a crucial role in reassembling all the molecules using both anabolism and catabolism, each cell has to have every single element and structure needed in it before starting to make a protein
Catabolism
a reaction in which you take a larger molecule to make something smaller
catabolic reactions break down molecules and release energy
glucose is stored as energy and is then catabolized and turned into ATP
catabolism gets its energy from animals
First, for example in a hamburger the meat is broken down into many molecules of amino acids by catabolism and gets mixed up with all the other amino acids of the other products as well as the bun, tomato and cheese