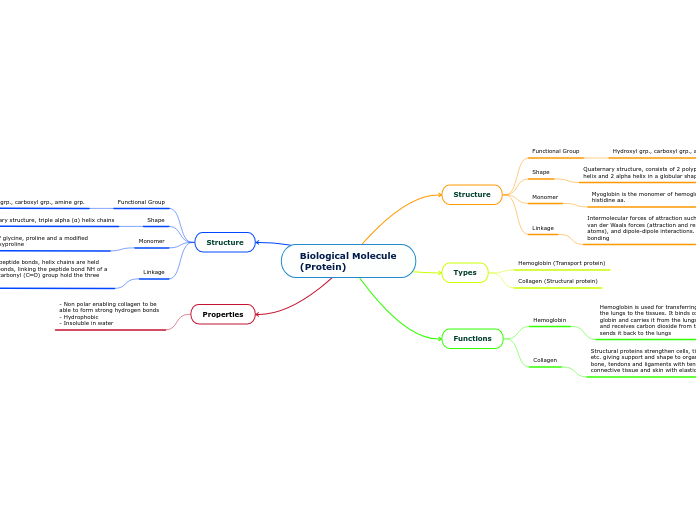
Biological Molecule (Protein)
Structure
Functional Group
Hydroxyl grp., carboxyl grp., amine grp.
Shape
Quaternary structure, consists of 2 polypeptide chains of beta helix and 2 alpha helix in a globular shape subunits
Monomer
Myoglobin is the monomer of hemoglobin, made up of histidine aa.
Linkage
Intermolecular forces of attraction such as hydrogen bonding, van der Waals forces (attraction and repulsions between atoms), and dipole-dipole interactions. As well as covalent bonding
Types
Hemoglobin (Transport protein)
Collagen (Structural protein)
Functions
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is used for transferring oxygen in your blood from the lungs to the tissues. It binds oxygen to the heme group in globin and carries it from the lungs to all tissues and organs, and receives carbon dioxide from the tissues and organs and sends it back to the lungs
Collagen
Structural proteins strengthen cells, tissues, organs, etc. giving support and shape to organisms. Provides bone, tendons and ligaments with tensile strength, connective tissue and skin with elasticity
Structure
Functional Group
Hydroxyl grp., carboxyl grp., amine grp.
Shape
Quaternary structure, triple alpha (α) helix chains
Monomer
Amino acids consisting of glycine, proline and a modified version of proline, hydroxyproline
Linkage
Monomers are held by peptide bonds, helix chains are held together by hydrogen bonds, linking the peptide bond NH of a glycine with a peptide carbonyl (C═O) group hold the three chains together
Properties
- Non polar enabling collagen to be able to form strong hydrogen bonds - Hydrophobic - Insoluble in water