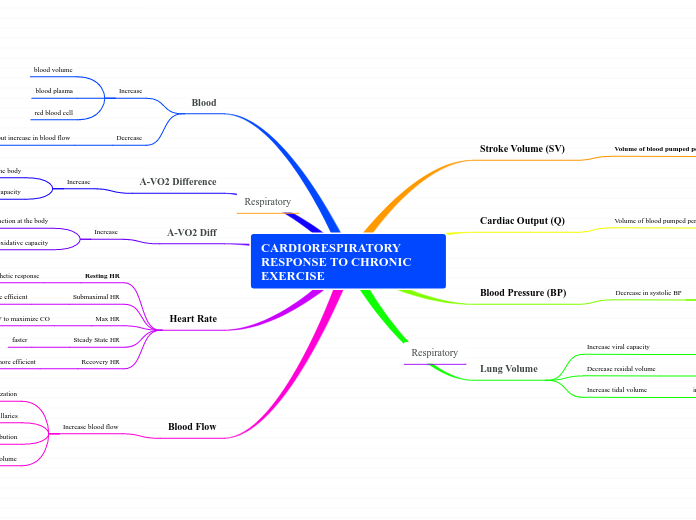
CARDIORESPIRATORY RESPONSE TO CHRONIC EXERCISE
Stroke Volume (SV)
Volume of blood pumped per stroke
Increase during rest, submaximal, maximal exercise
Increase in EDV
increase in blood plasma
Greater diastolic filing time
decrease heart rate
Increased heart contractility
Cardiac Output (Q)
Volume of blood pumped per minute
Q = SV x HR
Slight changes during rest, submaximal exercise
Increase during maximal exercise
increase in SV
Blood Pressure (BP)
Decrease in systolic BP
submax endurance exercise
chronic exposure to pressure
increase arteriole dilation at active muscle
Lung Volume
Increase viral capacity
max ammount of air expelled after max inspiration
Decrease residal volume
amounts of air that remains in the lung
Increase tidal volume
increase during maximal exercise
Blood
Increase
blood volume
blood plasma
red blood cell
Decrease
blood viscosity but increase in blood flow
A-VO2 Difference
Increase
due to increase O2 extraction in the body
increase oxidative capacity
A-VO2 Diff
Increase
due to increase o2 extraction at the body
increase oxidative capacity
Heart Rate
Resting HR
decrease due to increase in parasympathetic response
Submaximal HR
decrease because more heart more efficient
Max HR
decrease due to optimum SV to maximize CO
Steady State HR
faster
Recovery HR
decrease because heart more efficient
Blood Flow
Increase blood flow
increase capillarization
increase opening of existing capillaries
increase in blood redistribution
increase blood volume