Chemical Bonds
Ionic Bond
Ion-dipole interactions in water
Covalent Bond
Structure and Function of Cells
Prokaryotic Cells
Archaea
Circular chromosome
Cytoplasm
Bacteria
Plama Membrane
Gas Vacuole
Ribosomes
Inclusion bodies
Nucleoid
Periplasmic Space
Cell wall
Capsules
- slime layers
Fimbriae
Pili
Flagella
Endospore
Eukaryotic Cells
Animal
proteoglycan
Extracellular matrix
Desmosomes
Tight junctions
Gap junctions
Plants
Cell wall
Chloroplast
Central Vacuole
Plasmodesmata
Plastids
Both
Nuclear Envelope
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Plasma membrane
Ribosomes
Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
Mitochondria
Peroxisome
Microvilli
Cytoskeleton
Microfilaments
Intermediate filament
Microtubules
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Vesicles
Cytoplasm
Nonpolar
Van Der Waals
Hydrophobic Interactions
Polar
Examples in Biological Molecules
Peptide bond
Phosphodiester bond
Glycosylic linkage
Ester bond
Partially Charged Atoms
Hydrogen Bond
Water Properties
Cohesive behavior
High Specific Heat
High Heat of Vaporization
Denser as liquid than solid
Universal Solvent
Dipole-dipole Interaction
Biological Molecules
Nucleic acids
RNA
G/C and A/U
DNA
G/C and A/T
H-bonding through complitary base pairing forms DNA double helix
Nucleotides
Nitrogenous base
phosphate group
Phosphodiester link connects phosphites and sugars
5 carbon sugar
Lipids
Saturated
solid at room temperature
"saturated with Hydrogen"
Hydrophobic
Unsaturated
Liquid at room temperature
Double bonded carbon
Trans fats
removing double C bond and adding Hydrogen to convert cis to trans fat, however this incomplete formation of unsaturated to saturated fat is what leads to trans fat.
Carbohydrates
Isomers
Geometric Isomers
Enantiomers
Structural Isomers
Types of polysaccharides
structure
cellulose
storage
glycogen
starch
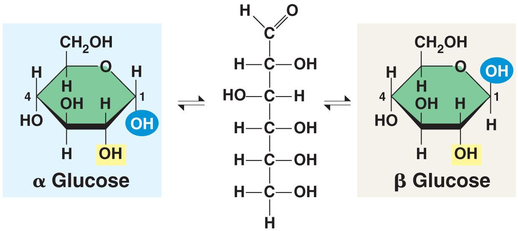
Beta Glucose
Alpha Glucose
Protiens
R groups
Polar
Non-polar
Acidic
Basic
Protein folding
Primary
Secodary
Alpha Helices
Beta pleated sheets
Tertiary
Quarternary
