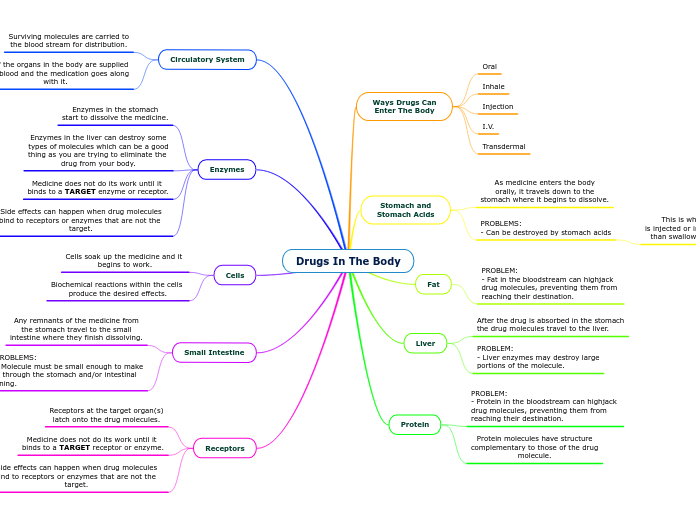
Drugs In The Body
Ways Drugs Can
Enter The Body
Oral
Inhale
Injection
I.V.
Transdermal
Stomach and
Stomach Acids
As medicine enters the body
orally, it travels down to the
stomach where it begins to dissolve.
PROBLEMS:
- Can be destroyed by stomach acids
This is why insulin
is injected or inhaled rather
than swallowed as a pill.
Fat
PROBLEM:
- Fat in the bloodstream can highjack
drug molecules, preventing them from
reaching their destination.
Liver
After the drug is absorbed in the stomach
the drug molecules travel to the liver.
PROBLEM:
- Liver enzymes may destroy large
portions of the molecule.
Protein
PROBLEM:
- Protein in the bloodstream can highjack
drug molecules, preventing them from
reaching their destination.
Protein molecules have structure
complementary to those of the drug
molecule.
Circulatory System
Surviving molecules are carried to
the blood stream for distribution.
All of the organs in the body are supplied
with blood and the medication goes along
with it.
Enzymes
Enzymes in the stomach
start to dissolve the medicine.
Enzymes in the liver can destroy some
types of molecules which can be a good
thing as you are trying to eliminate the
drug from your body.
Medicine does not do its work until it
binds to a TARGET enzyme or receptor.
Side effects can happen when drug molecules
bind to receptors or enzymes that are not the target.
Cells
Cells soak up the medicine and it
begins to work.
Biochemical reactions within the cells
produce the desired effects.
Small Intestine
Any remnants of the medicine from
the stomach travel to the small
intestine where they finish dissolving.
PROBLEMS:
- Molecule must be small enough to make
it through the stomach and/or intestinal
lining.
Receptors
Receptors at the target organ(s)
latch onto the drug molecules.
Medicine does not do its work until it
binds to a TARGET receptor or enzyme.
Side effects can happen when drug molecules
bind to receptors or enzymes that are not the target.