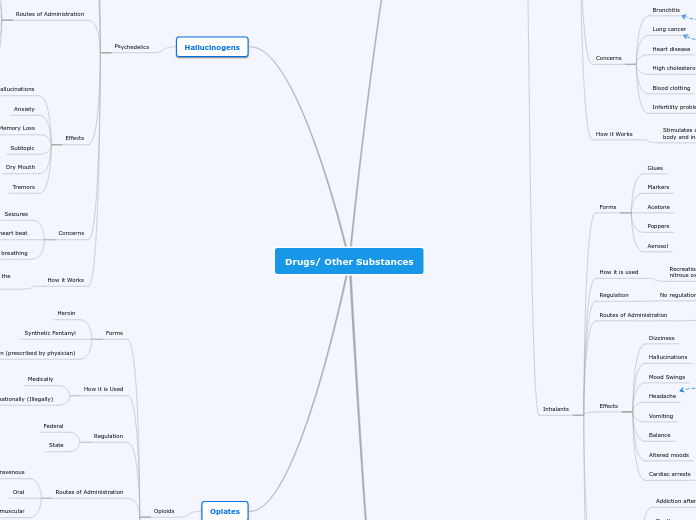
Drugs/ Other Substances
Depressants
Cannabis
Forms
CBD
THC
How it is Used
Recreation
Medical
Regulation
Illegal on Federal Level
Legal in 12 states for both medical and recreational use over 21 years old
Legal in 21 states for Medical use only age may differ state to state and depending on medical purpose
Routes of Administration
Smoking
Goes from lungs to blood stream and then into the brain
Edible
Goes into digestive track, then the blood stream, and then into the brain.
Effects
Pain Relief
Increase your dopamine
Increase or decrease anxiety levels
Red Eyes
Dry Mouth
Slow reaction time
Increased appetite
Concerns
Increase risk of Lung Cancer
Weakened Immune System
Bronchitis
How it Works
Increases the level of dopamine
Alcohol
Forms
Beer
Wine
Whisky
All in liquid form, more other types exists
How its used
Recreational
Regulation
Legal in all states in the US but must be over the age of 21
Routes of Administration
Ingestion/ oral
Effects
Slurred speech
Blurry Vision
Fatigue
Coordination
Concerns
Liver damage/ cancer
Heart damage
Birth Defects
Dependence
How it Works
It blocks receptors in the brain.
Tobacco
Forms
Chewing tobacco
Cigarettes
E-cigarettes
Pipe
Patches
Gum
Cigars
Etc.
How it is Used
Recreationally, and if genetically modified by scientists medically for some autoimmune diseases
Regulation
The FDA has regulation on tobacco products under the Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act. Must be at a certain age to purchase tobacco products, age varies state to state.
Routes of Administration
Topical, oral, inhalation, rectal, intranasal
Effects
Increased heart rate
Poor vision
Mood stimulation
Anxiety
Irritability
Dull smell and taste
Coughing
Concerns
Bronchitis
Lung cancer
Heart disease
High cholesterol
Blood clotting
Infertility problems
How it Works
Stimulates adrenal glands which release epinephrine into the body and increases the level of dopamine.
Inhalants
Forms
Glues
Markers
Acetone
Poppers
Aerosol
How it is used
Recreationally mostly, however there is one medical use of nitrous oxide (laughing gas)
Regulation
No regulation
Routes of Administration
Inhalation
Effects
Dizziness
Hallucinations
Mood Swings
Headache
Vomiting
Balance
Altered moods
Cardiac arrests
Concerns
Addiction after long term use
Death
Loss of concentration
Short term memory
Hearing loss
Muscle spasms
Permanent brain damage
How it Works
Depends on the inhalant, some have a similar effect on the brain as alcohol, others increase the size of blood vessels making your heart race.
Stimulants
Caffeine
Forms
Energy Drinks
Coffee
Tea
Pills
Soft Drinks
Etc.
How it is used
Both Medical and Recreational
Regulation
FDA requires labeling on any product that has caffeine in it.
Routes of Administration
Drinking, chewing (gum), so orally
Effects
Alertness
Rapid Heart Beat
Headache
Jitters
Decreased risk of oral cancer
Concerns
Pregnancy issues
Fertility problems
Effect bones
How it Works
The human body has receptors in the brain called adenosine, and caffeine helps to fool the adenosine receptors which usually bond with adenosine the brain makes. Caffiene helps block this bond from happening which prevents fatigue or exhuastion.
Methamphetamine
Forms
Crystal Meth
Glass/ Ice
Speed
Subtopic
How it is used
Medically
Recreationally
Regulation
Under Schedule II of the Controlled Substances Act
Routes of Administration
Smoking
Pill
Snorting
Injecting/dissolving
Effects
More energy
Increased breathing
Increased attention
Hypothermia
Increased perspiration
Panic attacks
Increased violence
Dry mouth
Weight Loss
Effects sleeping patterns
Concerns
Dependence
Paranoia
Hallucinations
Stroke
How it works
It increases the level of dopamine released in the brain. However, this excess dopamine is not stored or "recycled" for later. It creates an overstimulated brain that can only be replaced by a wave of unpleasant feelings which trigger the user to use again to feel good again.
Hi
Forms
How
Hallucinogens
Psychedelics
Forms
PCP
Salvia
Benadryl
Nightshade
How it is Used
Recreationally
Religously
Regulation
Federal has it under a Schedule I drugs
Routes of Administration
Oral
Inhalation
Intravenous
Intramuscular
Rectal
Transdermal
Effects
Hallucinations
Anxiety
Memory Loss
Subtopic
Dry Mouth
Tremors
Concerns
Seizures
Decreased heart beat
Shallow breathing
How it Works
Stimulates the serotonin receptor 2A in the brain making the user feel an altered state of being.
Opiates
Opioids
Forms
Heroin
Synthetic Fentanyl
Pain medication (prescribed by physician)
Oxycodone, morphine, hydrocodone... etc.
How it is Used
Medically
Recreationally (Illegally)
Regulation
Federal
State
Routes of Administration
Intravenous
Oral
Intramuscular
Effects
Drowsiness
Shallow breathing
Nausea
Constipation
Concerns
Very addictive
Loss of consciousness
Shallow breathing
Slow Heart Beat
How it Works
Floods the brain with dopamine and blocks receptors to the brain, helping with reduction in pain.