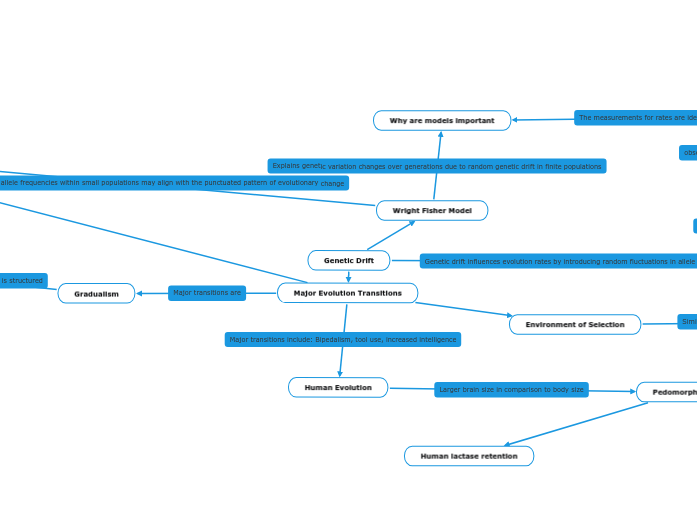
The measurements for rates are identified by this model
Similar environments lead to organisms having similar solutions to challenges
Larger brain size in comparison to body size
Major transitions are
observed genetic frequencies and the model's predictions helps assess and measure the rates of evolution within a population
Major transitions include: Bipedalism, tool use, increased intelligence
relatively rapid changes in allele frequencies within small populations may align with the punctuated pattern of evolutionary change
Explains genetic variation changes over generations due to random genetic drift in finite populations
Influences how the anatomy is structured
Influences how the anatomy is structured.
the structure of the tree determined by the analysis of genetic data to infer evolutionary divergence
provides a baseline for understanding how genetic variation is maintained or changed in non-evolving populations
Genetic drift influences evolution rates by introducing random fluctuations in allele frequencies within populations.