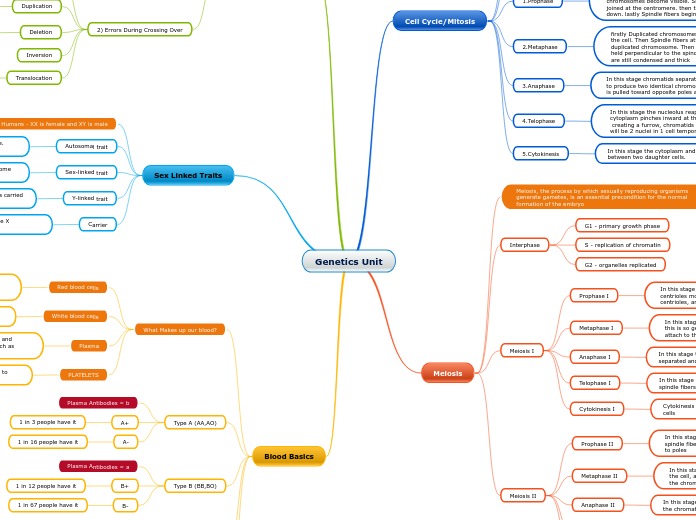
Genetics Unit
Cell Cycle/Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle when replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the number of chromosomes is maintained.
Interphase
G1 - primary growth phase
S - replication of chromatin
G2 - organelles replicated
1.Prophase
In this stage Centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell, then Chromatins condense into chromosomes and duplicated chromosomes become visible. Sister chromatids also are joined at the centromere. then the nuclear membrane breaks down. lastly Spindle fibers begin to extend from the centrioles
2.Metaphase
firstly Duplicated chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell. Then Spindle fibers attach at the centromere of each duplicated chromosome. Then the Duplicated chromosome is held perpendicular to the spindle fibres. lastly Chromosomes are still condensed and thick
3.Anaphase
In this stage chromatids separate at the centromere
to produce two identical chromosomes. Then Each chromatid is pulled toward opposite poles as spindle fibres shorten
4.Telophase
In this stage the nucleolus reappears, spindle fibers dissapear, cytoplasm pinches inward at the equator
creating a furrow, chromatids uncoil and elongate, and there will be 2 nuclei in 1 cell temporarily.
5.Cytokinesis
In this stage the cytoplasm and organelles are distributed
between two daughter cells.
Meiosis
Meiosis, the process by which sexually reproducing organisms generate gametes, is an essential precondition for the normal formation of the embryo
Interphase
G1 - primary growth phase
S - replication of chromatin
G2 - organelles replicated
Meiosis I
Prophase I
In this stage Chromatin condenses into chromosomes, centrioles move to opposite poles, spindle fibers form from centrioles, and the nuclear membrane breaks down
Metaphase I
In this stage the tetrads line up along the equator randomly this is so genetic variation can occur, then the spindle fibers attach to the pair of sister chromatids
Anaphase I
In this stage the chromosome pairs are
separated and are pulled to opposite ends
Telophase I
In this stage the nuclear membrane reforms and the
spindle fibers retract.
Cytokinesis I
Cytokinesis occurs forming two genetically different daughter cells
Meiosis II
Prophase II
In this stage the nuclearmembrane begins to break down, spindle fibers begin to form, and the centrioles begin to move to poles
Metaphase II
In this stage the chromosome pairs align along the equator of the cell, and then the Spindle fibers attach to centromeres of the chromatids
Anaphase II
In this stage the spindle fibers pull
the chromatids apart
Telophase II
In this stage the Nuclear membrane reassembles, chromosomes decondense, and the spindles disappear
Cytokinesis II
Four genetically different daughter cells form
Mistakes in Meiosis
1) Errors During Chromosome Division
this error occurs when chromosomes in meiosis do not
divide properly, which results in gametes with extra or missing chromosomes
Monosomy - One missing chromosome
Results in Turner’s Syndrome
Trisomy - One extra chromosome
Results in Klinefelter Syndrome
Polysomy - more than 1 extra chromosome
Results in Down Syndrome
2) Errors During Crossing Over
This Occurs when DNA is not exchanged
properly during recombination
Duplication
Results in an extra
copy of the gene
Deletion
Results in a loss of
genetic information
Inversion
Translocation
Results in a Gene not being able to be
expressed properly
Sex Linked Traits
Humans - XX is female and XY is male
Autosomal trait
In this trait the gene is carried on a non sex chromosome. which in presented in two copies in both sexes.
Sex-linked trait
In this trait genes are carried on one of the sex chromosome that is in both sexes.
Y-linked trait
this trait is in humans, which talks about a gene that is carried on the Y chromosome
Carrier
A female who “carries” the recessive allele on one X chromosome
Blood Basics
What Makes up our blood?
Red blood cells
This cell is the most abundant cells in our blood. They are produced in the bone marrow and have a protein called hemoglobin that carries oxygen to our cells.
White blood cells
Are part of the immune system and help protract us from infections and diseases.
Plasma
This part of the blood contains electrolytes, nutrients and vitamins, hormones, clotting factors, and proteins such as antibodie.
PLATELETS
these are tiny blood cells that help your body form clots to stop bleeding.
Type A (AA,AO)
Plasma Antibodies = b
A+
1 in 3 people have it
A-
1 in 16 people have it
Type B (BB,BO)
Plasma Antibodies = a
B+
1 in 12 people have it
B-
1 in 67 people have it
Type AB (AB)
Plasma Antibodies = NONE
AB+
1 in 29 people have it
AB-
1 in 167 people have it
Type (OO)
Plasma Antibodies = ab
O+
1 in 3 people have it
O-
1 in 15 people have it