History Of Earth
How do we determine the age of Earth?
Sources
Notebook
Presentation
Claim
Similar coastlines
Fossil records
Age and typeof rocks
Evidence
Radioactive decay scientists compare the proportions of the original new isotopes to determine the absolute age of the rocks
Scientists list the order of rocks the newer layers will be on top of the older ones
Absolute age is an exact number like this rock is 100 years old
Connections
A sandwich has different layers like the earth first the bread then the meat etc.
Vocab
Relative Dating - Determining the age of an object by comparing its age to another object.
Absolute Dating-determining the age of an object comparing its age to another object
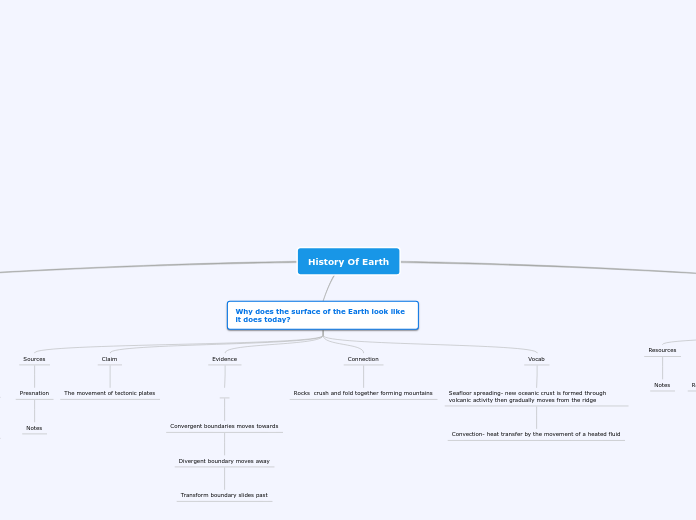
Why does the surface of the Earth look like it does today?
Sources
Presnation
Notes
Claim
The movement of tectonic plates
Evidence
Convergent boundaries moves towards
Divergent boundary moves away
Transform boundary slides past
Connection
Rocks crush and fold together forming mountains
Vocab
Seafloor spreading- new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity then gradually moves from the ridge
Convection- heat transfer by the movement of a heated fluid
What changes do rocks go through?
Resources
Notes
Claim
Rocks go through a never ending rock cycle
Connection
The rock I am presenting for is a metamorphic rock which is Slate
Vocab
Sedimentary Rocks - When sediment deposits harden after being compressed and cemented together
Metamorphic Rocks - The rock existing from a change of heat, pressure, and chemical processes.
Igneous Rocks - Forms when magma cools and hardens
Evidence
All rocks start as Magma then Crystalize in a Igneous rock and then separate from them
Sedimentary rocks are classified by type and size
Metamorphic rocks are classified by texture
Igneous rocks are classified by location of magma