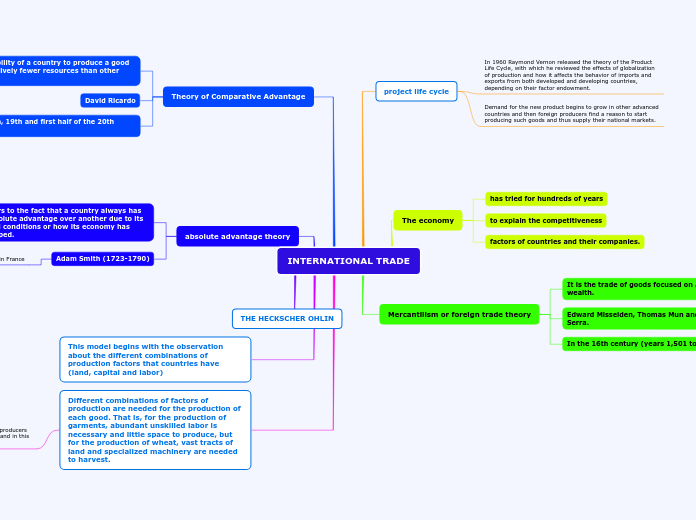
INTERNATIONAL TRADE
project life cycle
In 1960 Raymond Vernon released the theory of the Product Life Cycle, with which he reviewed the effects of globalization of production and how it affects the behavior of imports and exports from both developed and developing countries, depending on their factor endowment.
Demand for the new product begins to grow in other advanced countries and then foreign producers find a reason to start producing such goods and thus supply their national markets.
The economy
has tried for hundreds of years
to explain the competitiveness
factors of countries and their companies.
Mercantilism or foreign trade theory
It is the trade of goods focused on generating wealth.
Edward Misselden, Thomas Mun and Antonio Serra.
In the 16th century (years 1,501 to 1,600)
Theory of Comparative Advantage
It is the ability of a country to produce a good using relatively fewer resources than other countries.
David Ricardo
in the 18th, 19th and first half of the 20th century
absolute advantage theory
It refers to the fact that a country always has an absolute advantage over another due to its natural conditions or how its economy has developed.
Adam Smith (1723-1790)
In the second half of the 18th century in France
THE HECKSCHER OHLIN
This model begins with the observation about the different combinations of production factors that countries have (land, capital and labor)
Different combinations of factors of production are needed for the production of each good. That is, for the production of garments, abundant unskilled labor is necessary and little space to produce, but for the production of wheat, vast tracts of land and specialized machinery are needed to harvest.
Demand for the new product begins to
grow in other advanced countries and then foreign producers find a reason to start the production of such goods and in this way. supply their national markets