Memory (Human)
Short-term memory
working memory
Sensory memory
Sight
Sound
Taste
Touch
Smell
Long-term memory
Explicit Memory-Conscious awareness of a person.
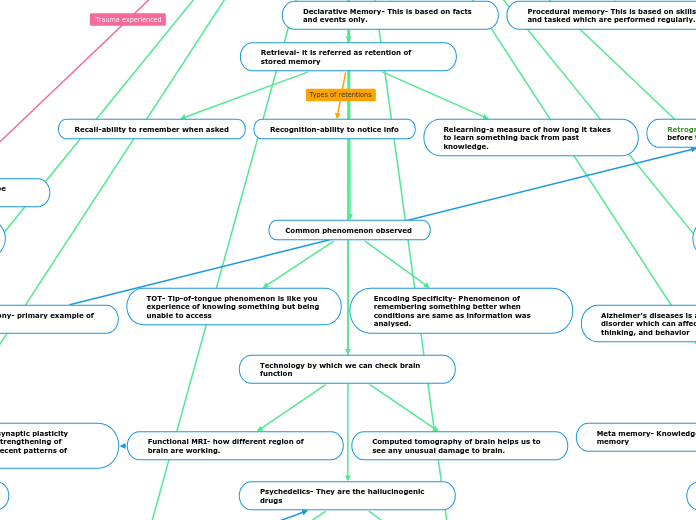
Declarative Memory- This is based on facts and events only.
Implicit Memory- unconscious awareness of a person.
Procedural memory- This is based on skills and tasked which are performed regularly.
Storage
Rehearsal
Maintenance- repetition with little of no interpretation.
Elaborative- when the stimulus maybe linked with other information.
Retrieval- it is referred as retention of stored memory
Recall-ability to remember when asked
Recognition-ability to notice info
Relearning-a measure of how long it takes to learn something back from past knowledge.
Amnesia-inability to remember the information.
Retrograde-loss of memory were formed before the event
Anterograde- where you can't form new memories after the event
False memory-when our brain is traumatized, so cannot recollect memory right.
tragic event- This could lead into false sensations.
Eye witness testimony- primary example of it.
Common phenomenon observed
TOT- Tip-of-tongue phenomenon is like you experience of knowing something but being unable to access
Encoding Specificity- Phenomenon of remembering something better when conditions are same as information was analysed.
Memory deterioration- This is often normal with aging but could be observed in diseased young individuals.
Alzheimer's diseases is a progressive disorder which can affects memory, thinking, and behavior
Multiple Sclerosis- a chronic disease that affects the central nervous system causing poor coordination.
Biology of memory
LTP and Hipocampus-a stable facilitation of synaptic potentials after high-frequency synaptic activity.
LTP and glutamate-synaptic plasticity where a persistent strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity occurs.
Technology by which we can check brain function
Functional MRI- how different region of brain are working.
Computed tomography of brain helps us to see any unusual damage to brain.
Memory overtime when you grow-up
Meta memory- Knowledge of our own memory
Knowledge and related inferential processes, spanning from simple types of perception to complex forms of thinking, are referred to as cognition.
Hypnosis- process to getting someone out of their conscious state.
Fact- It can help from anxiety, depression, phobias, and addiction. It can also be used to manage pain and improve sleep.
Myth- hypnotist cannot control the person's mind or make them do anything they don't want to do
Psychedelics- They are the hallucinogenic drugs
Marijuana- Also know as pot and make you "high", and unconscious.
LSD- Chemically synthesised drug which binds to specific brain cell receptors and alters how the brain responds to serotonin,
How sleep affects memory and the neural coordination
A person needs 8 hrs of sleep to function well on average.
Some humans have mutations on ADRB1 and can actually work optimally on 4 hrs of sleep on average.
Stimulants- Anything that can stimulate nervous system
Nicotine- Most common type (people getting from cigarettes)
Cocaine- It is most powerful natural stimulant which can make person euphoric and enhance mental and physical capacity.
Amphetamines- They are subjective to use of a person.
Increased in dopamine ruse and makes person more conscious.
This is extensively used in prescription drugs used for ADHD.