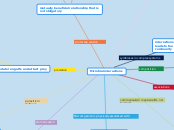
Microbial interactions
various ways such as
microorganism remains outside other organisms
microorganim found within other organism
microorganisms lives both on the inside and the outside organisms
intermittent, cyclic or permanent
obligatory associations that provides benefit to both partners
secrete cellulases which metabolize cellulose used by insects
Protozoan-termite relationship
guts of insects
algae protect fungi from excess light as well as provide mineral, water and firm substratum
can obtain nutrients from alga by hyphal projections and respiration
lichen
zooxanthellae
energy needs and protect algae from uv
tube worm binds hydrogen sulphide to hemoglobin and transport to bacteria
to synthesize reduced organic material that supplied to the worm
hydrothermal vent communities
anoxic, have high concentrations of hydrogen sulfide and temperatures of 350 degree celcius
methane based mutualism
to support nutritional needs
methane -vent musels and sponges
bacteria provides vitamin to insects wheras insect provide habitat to bacteria
metabolize cellulose to smaller molecules
by ruminants
mutually beneficial relationship that is not obligatory
3-chlorobenzoate
three different microorganisms
quorum sensing
communicate as they form associations with plants and animals
predator engulfs and attact prey
vampirococcus causes lysis of prey
prey provides protective environmentfor the prey and predators mineralize organia matter
fungi that traps nermatodes
one organisms benefits from host
human diseases, parasitic fungi and an algae as well as biocontrol use
releaese specific compound that harm others
antibiotics, bacteriocins, antibacterial peptides and acidic fermentation products
waste products of one microorganism serves as substrates for another
one microorganism modifies the environmentsuited for others
nitrification, common nonpathogenic strain and succession of microorganisms in an environment
different organisms within population or community which try to acquire the same sources
competitive exclusion principle
if two populations overlap too much in terms of their resourse use, then other is excluded