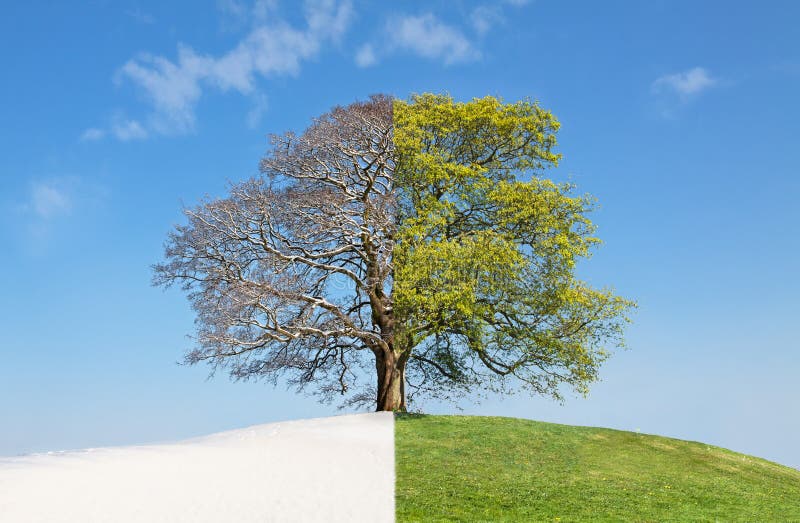
SEASONAL AFFECTIVE DISORDER
Desmethylsertraline
α-hydroxyketone
Excreted in the urine and faeces
PRESENTATION /
SYMPTOMS

General symptoms
Anhedonia
Feeling Worthless
Suicidal thoughts
Feeling Stressed/Anxious
Difficulty Concentrating

Spring/Summer S-SAD
Poor Appetite → Weight Loss
Insomnia
Agitation/Anxiety
Increased Irritability

Autumn/Winter SAD
Overeating → weight gain
Hypersomnia
Fatigue - Low energy
Social Withdrawal (hibernating)
DIAGNOSIS

Diagnostic Criteria
SAD and S-SAD Specific Symptoms
Consecutive Seasonal
Depressive Episode ≥ 2yrs
Frequent Depression in
Specific Season(s)

Final Diagnosis
SAD
More common
S-SAD
less common

GP / Psychiatrist
Seasonal Pattern Assessment
Questionnaire (SPAQ)
Symptom Evaluation
No Current Blood Tests / Scans

Differential Diagnosis
Hypothyroidism
Hypoglycaemia
Infectious Mononucleosis
Viral Infections
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY

Circadian Rhythm
Physiology
RHP axis
Light-triggered
Subtopic

Melatonin
Overproduction
Lack of Sunlight
Poor Intensity
Underproduction
Prolonged Sunlight
High Intensity

Serotonin
Increased SERT
Increased 5% (W)
↑ Serotonin Reuptake
↓ Serotonin Activity
Vitamin D Deficiency
Serotonin Production ↓
Serotonin Firing
Psychological Treatment
Structure
6-20 Sessions
Inter-Patient Variability
30-60 Mins Session
Once Weekly/Every Two Weeks
Subtopic
Purpose
Problem Breakdown
Thoughts
Unrealistic?
Unhelpful?
Feelings
Dealing with them Strategically
Actions
Self-Guided or Instructed
Groups or One to One
Self-Guided OR Instructed
OVERVIEW

Definition
"Specifier" of MDD / BPD
Seasonal Pattern to disease
Two Seasonal Types
Spring / Summer (S-SAD)
Autumn / Winter (SAD)

History
1980s Research
Norman Rosenthal
Alfred J. Lewy
Tom Wehr
Risk Factors
Female (4:1)
Shift Workers / Nurses
Distance from Equator
Northern Latitudes
Clinical
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy
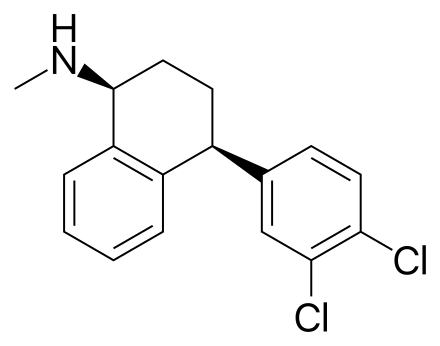
Antidepressants First line SSRIs e.g Sertraline

Limited evidence of efficacy

Metabolism
CYP3A4
CYP2D6
CYP2C19
CYP2B9

Interactions
Grape fruit juice
CYP3A4 inducer
Triptans
Other antidepressants e.g. TCAs, MAOIs
Serotonin syndrome
Drugs that increase hyponatraemia risk e.g. lithium, carbamazepine
Drugs that increase bleeding risk e.g. NSAIDs, DOACs
Sertraline inhibits uptake of 5-HT into platelets
Impaired platelet aggregation

Side Effects
Anxiety
5-HT2A/5-2C
Insomnia
5-HT2A/2C
Sexual dysfunction
5-HT2A/2C
Nausea
5-HT3
Diarrhoea
5-HT4
Headache
Dry mouth
Mechanism
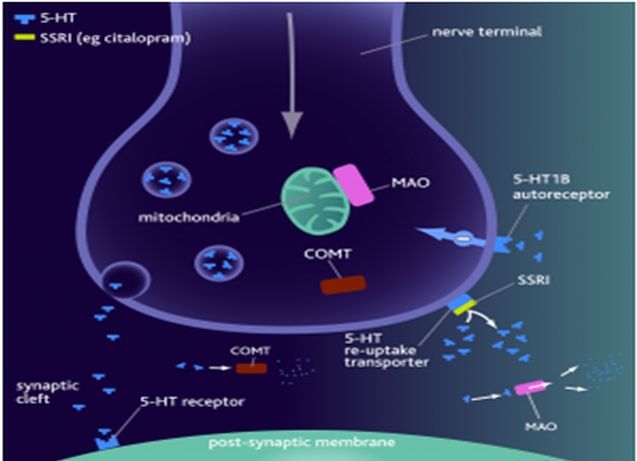
Increase synaptic 5-HT levels
Inhibit SERT
Downregulate 5-HT1A
Initiate treatment 4-6 weeks before symptoms

Counselling
Caution in pregnancy
Discuss with doctor
Not recommended in the first three months
Loss of pregnancy
Congenital birth defects
Do not stop abruptly
Gradual withdrawal
Take in the morning
Light Therapy
Improve Mood
Reduce Melatonin Production
Sleep Hormone
Increase Serotonin Production
Mood Hormone
Contraindications:
Eye Condition/Eye Damage
Photosensitivity
Light Box
Special Lamp
Improves Mood during the Winter Months
30Mins - 1 Hour Exposure every Morning
Side Effects:
Blurred Vision
Tiredness
Headache
Eye Strain
Agitation
HSE SilverCloud
Non-Pharmacological Advice
Increase Natural Sunlight Exposure
Increase Physical Activity
Healthy, Balanced Diet
Talk to Family and Friends about SAD Diagnosis