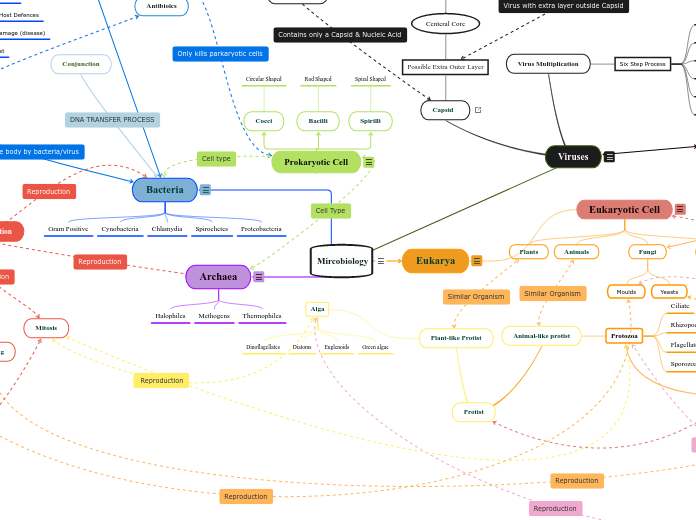
Mircobiology
Bacteria
Gram Positive
Cynobacteria
Chlamydia
Spirochetes
Proteobacteria
Archaea
Halophiles
Methogens
Thermophiles
Eukarya
Eukaryotic Cell
Plants
Animals
Fungi
Moulds
Yeasts
Protista
Prokaryotic Cell
Cocci
Circular Shaped
Bacilli
Rod Shaped
Spirilli
Spiral Shaped
Asexual Reproduction
Conjunction
Protist
Plant-like Protist
Alga
Dinoflagellates
Diatoms
Euglenoids
Green algae
Animal-like protist
Protozoa
Ciliate
Rhizopod
Flagellate
Sporozoan
Binary Fisson
Mitosis
Sexual Reproduction
Chlamydomonas
Budding
Spore Formation
Sporangia
Produces Spores
Viruses
Capsid
Possible Extra Outer Layer
Centeral Core
Genetic Material
RNA or DNA
Virus Multiplication
Six Step Process
1. Adsorbtion
2. Penetration
3. Uncoating
4. Synthesis
5. Assembly
6. Release
Naked Virus
Eveloped Virus
Infection
Developing of Infection
1. Finding portal of entry
2. Attaching Firmly
3. Surviving Host Defences
4. Causing Damage (disease)
5. Exiting Host
Antibioics
Treats Bacterial Infection
"Good" Bacteria
Skin Bacteria
Digestive tract bacteria
Communicable Diseases
Infections transmitted from one person to another
Direct Transmisson
Indirect Transmisson
Defences of the Immune System
Physical & Chemical Barriers
Resident micro-organisms
Inflammation
Immune cells and proteins
Fever
Parasites
Diseases in humans and other animals
Giardiasis
Disease in humans caused by a protozoan
Invloves formation of cysts
In cyst form, protozoan is protected and can be spread in air and water
Molaria
Spread by Mosquitos
Anti-Fungal Agents
Used to treat fungal infections
Virus caused disease
Caused by a virus infecting cells
Some viruses only infect plants
Some viruses only infect humans
The Flu
Caused by Influenza Virus
Chickenpox
The Common Cold
AIDS
Some viruses only infect bacteria
called Phages