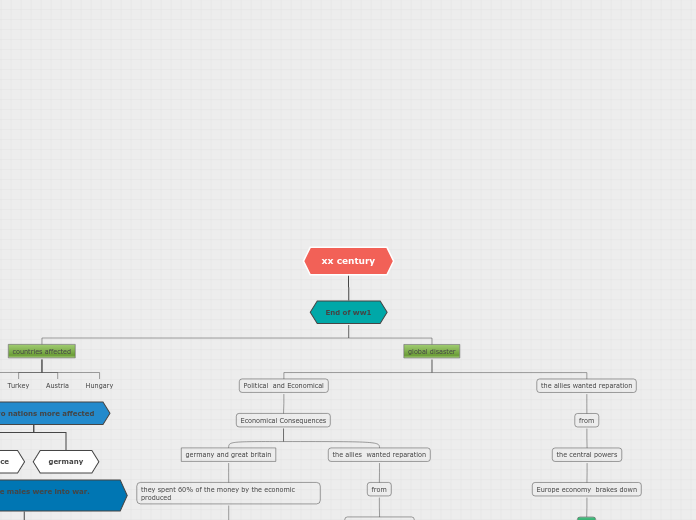
xx century
End of ww1
countries affected
Russia
Turkey
Austria
Hungary
global disaster
Political and Economical
Economical Consequences
germany and great britain
they spent 60% of the money by the economic produced
countries had to
raise the taxes
and borrow the money
to the citizens
the allies wanted reparation
from
the central powers
the allies wanted reparation
from
the central powers
Europe economy brakes down
NO
jobs
companies
political consequences
end of four monarchies
russia
germany
austria
ottoman empire
nothing to sell
the two nations more affected
france
germany
80 porcent of the males were into war. age(15-49)
average
country
british empire
france
italy
united states
killed or died
908,371
1,357,800
650,000
116,516
some countries lose territories
central powers
great depression
consequences
unemployment rose
25%
and
homelessnes increased
economy
650 banks had failed
in 1932 and 1933
the country only produced $56.4 billion
politics
affect capitalism
presidents
president herbert
had failed in votes
franklin roosevelt
he promised the depression ends
relationship with ww1
economic depression
1930s 20th century
longest and deppest widespread depression
stock market crash
the gold standard
decreased international lending and tariffs
banking panics and
monetary contaction
1920-1929
1930-1932
september 4 1929
culture of the 1920s
literature
reading
became very popular
Magazines
books
many authors
won
many novels
news papers
arts
surrealism
develop
decalcomania
frottage
fumage
grattage
parsemage
after ww1
artist
andree masson
art deco
materials
aluminium
stainless
lacquer
inlaid woad
sharkin
zebra skin
music
know as the
jazz age
louis amstrong
kid ory
ouxe ellington
king oliver
american artist
maxfield parrish
coles phillips sally
broad way musicals
people went and pay many dollars$
shows
sally
no, no nonette
f.scott fitzgerald ,dorothy parker ,edith wharton,wila cather
rise of nationalism and facism
characteristics
focused on military power and nationalism
this regime is similar to the socialist regime
the economy was controlled by the state
racism and discrimination are two facist regimes that are very common
the state was more important than the individual in facist regimes
they think all the nations struggle for power
facism
purpose
the facist party porpuse was to promince violence and intimidate the people
the facist regime have a strong centralized state or national goverment, they took all the decisions in goverment.
meaning
political and social movement in italy during the world war 1
benito mussolini
he form the political group with other liders
causes of ww1
causes
mutual defense alliances
russia and serbia -austria and hungary-france and russia-britain and france also belgium
they were defense agreements and many treatments between countries.
imperialism
the increase of competition
africa and asia
were points of contention
European countries
causes
militarism
they increased in militarism
helped pushing the countries into war
asassination of archduke franz ferdinad
the black hand
their first attempt to killed him failed
nationalism
led directly to the war
countries tryed to prove their dominace and power