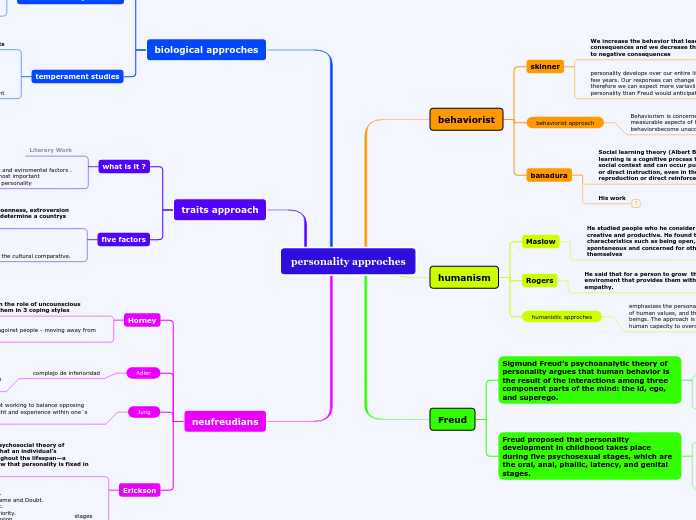
personality approches
behaviorist
skinner
We increase the behavior that lead to positive consequences and we decrease the behaviors that lead to negative consequences
personality develops over our entire life, not only in th first few years. Our responses can change over new situations therefore we can expect more variavility over time in personality than Freud would anticipate.
behaviorist approach
Behaviorism is concerned primarily with theobservable and measurable aspects of human behavior. Therefore when behaviorsbecome unacceptable, they can be unlearned.
banadura
Social learning theory (Albert Bandura) posits that learning is a cognitive process that takes place in a social context and can occur purely through observation or direct instruction, even in the absence of motor reproduction or direct reinforcement.
His work
humanism
Maslow
He studied people who he consider to be healthy creative and productive. He found that they had similar characteristics such as being open, creative, loving, spontaneous and concerned for others and accepting of themselves
Rogers
He said that for a person to grow they need an enviroment that provides them with genuineness and empathy.
humanistic approches
emphasizes the personal worth of the individual, the centrality of human values, and the creative, active nature of human beings. The approach is optimistic and focuses on the noble human capacity to overcome hardship, pain and despair.
Freud
Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic theory of personality argues that human behavior is the result of the interactions among three component parts of the mind: the id, ego, and superego.
Conflicts among these three structures, and our efforts to find balance among what each of them “desires,” determines how we behave and approach the world.
He believed taht the ego seeks to rstore balance through various protective measures known as defense mechanisms
denial, displacement, projection, reaction formation, regression,repression, rationalization, sublimation.
Freud proposed that personality development in childhood takes place during five psychosexual stages, which are the oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital stages.
which are the oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital stages.
In describing human personality development as psychosexual Freud meant to convey that what develops is the way in which sexual energy of the id accumulates and is discharged as we mature biologically. (NB Freud used the term 'sexual' in a very general way to mean all pleasurable actions and thoughts).
biological approches
Minnesota study of twins
from 1979 to 1999
350 pairs of twins were separated and raised unaware of their siblings
identical twins have similar personality and physiological traits weather they were
temperament studies
temperaments
start developing early in our lives and there are three types, easy difficult and slow to warm up, to identify it when we are babies.
body type and temperament
ectomorph
mesomorph
endomorph
traits approach
what is it ?
Literary Work
personality is shaped by both genetic and eviromental factors . culture in wich we live is one of the most important enviromental factors that shapes our personality
five factors
conscientiousness, neuroticism, poenness, extroversion and agreeableness, these help to determine a countrys personality differences
first approach is the cultural comparative.
the second is the indigenous
the third is the combined aproach
neufreudians
Horney
The theories are based on the role of uncounscious anxiety and she divided them in 3 coping styles
-moving towards, -moving agoinst people - moving away from people
Adler
complejo de inferioridad
For some people, the sense of inferiority serves as a positive motivating factor, as they strive to improve themselves in an effort to neutralize the negative feelings of inferiority. Some, however, become dominated—and, as a result, crippled—by an overwhelming sense of inadequacy.
Jung
Analytical psychology is not working to balance opposing forces of unconsious thought and experience within one´s personality
He prpposed to attitudes or approaches to work life extroversion and introversion. This ideas are considered his most important contributions to the field of psychology
Erickson
Erikson later proposed a psychosocial theory of development, suggesting that an individual’s personality develops throughout the lifespan—a departure from Freud’s view that personality is fixed in early life.
Erikson emphasized the social relationships that are important at each stage of personality development, in contrast to Freud’s emphasis on sex. Erikson identified eight stages, each of which represents a conflict or developmental task. The development of a healthy personality and a sense of competence depend on the successful completion of each task.
stages
Stage 1: Trust vs. Mistrust.
Stage 2: Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt.
Stage 3: Initiative vs. Guilt.
Stage 4: Industry vs. Inferiority.
Stage 5: Identity vs. Confusion.
Stage 6: Intimacy vs. Isolation.
Stage 7: Generativity vs. Stagnation.
Stage 8: Integrity vs. Despair.