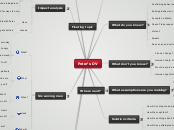
Peter's DV
Problem type
Change something
What do you know?
Controlling behaviour
Bullying behaviour
Accepts no blame
Doesn't take responsibility
Violent
Swears
Says sorry and will never do it again
What don't you know?
Can he change?
How can I help him?
Would a course help?
How can I get him to go to a course?
What assumptions are you making?
That he can change
That he is in danger of perpetrating DV
That it is partly my fault
Solution criteria
He will not stop me doing things
He will accept fault
He will see things don't always go his way
He will have strategies to solve problems
He will treat me with respect
Root cause analysis
He thinks it's all about him
His ASD
Cause
Cause
Cause
I've let him away with too much
Because I don't want him sad
Subtopic
Because I love him so much
Cause
Impact analysis
Me
He scares me
It makes me not like him
I feel like a bad parent
It makes me search for ways to help
Dave
He fights with Peter
Joanna
She gets bullied
Six serving men
What?
When he doesn't get his own way
When he's hungry
When he's in a bad mood
What not?
When he's in a good mood
Why?
He may use DV with future partners
He bullies me
Why not?
Why not?
When?
When?
When not?
When not?
How?
How?
How not?
How not?
Where?
Where?
Where not?
Where not?
Who?
Who?
Who not?
Who not?
Analogies
What is it like?
Be the problem
Insight