Electromagnetic Waves
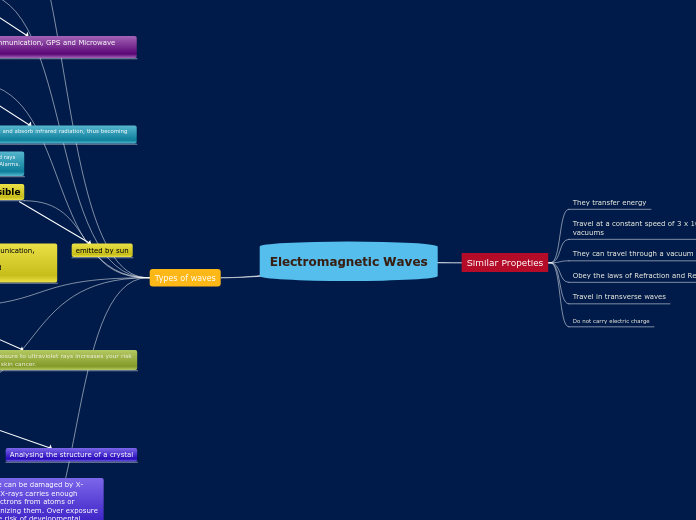
Similar Propeties
They transfer energy
Travel at a constant speed of 3 x 10^8 ms-1 in vacuums
They can travel through a vacuum
Obey the laws of Refraction and Reflection
Travel in transverse waves
Do not carry electric charge
Types of waves
Radio Waves
30Hz-300GHz
Emitted by lightning and astronomical objects
Generated by radio transmitters.
Used to transmit information
E.g. radio,radar and RC vehicles
A strong enough beam of radio waves can penetrate the eye and heat the lens enough to cause cataracts.
Mircowaves
300MHz-300GHz
Emitted by warm objects
Used in Communication, GPS and Microwave ovens
Infrared
430THz-300GHz
Emitted by warm objects
All objects emit and absorb infrared radiation, thus becoming hotter.
Commonly used for heat detectors, Infrared rays
are used in Thermal cameras and Intruder Alarms.
Other usages are Remote Controls.
Visible
used for optical fibres in telecommunication, lasers
for medical and industrial uses and photosynthesis
emitted by sun
Ultraviolet
used to detect forgery in bank notes, artificial suntanning
sterilising and disinfecting equipment
emitted by sun
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays increases your risk of developing skin cancer.
X-Ray
Emitted by high energy electrons
Used as a diagnostic tool in medicine and dentistry
Analysing the structure of a crystal
Airport baggage scanner
Checking flaws in metals
Living cells and tissue can be damaged by X-rays. This is because X-rays carries enough energy to remove electrons from atoms or molecules, thereby ionizing them. Over exposure to X-rays increase the risk of developmental problems and cancer. The risk of radiation is greater to a fetus, so pregnant patients are advised to avoid exposure to X-rays.
Gamma Ray
Emitted by radioactive nuclei
To kill cancer cells
Sterilising medical equipments
Able to destroy brain tumours
Gamma Rays are even more harmful to living cells and tissue than X-rays. This is because Gamma Rays carry enough energy to remove electrons from atoms or molecules, thereby ionizing them.