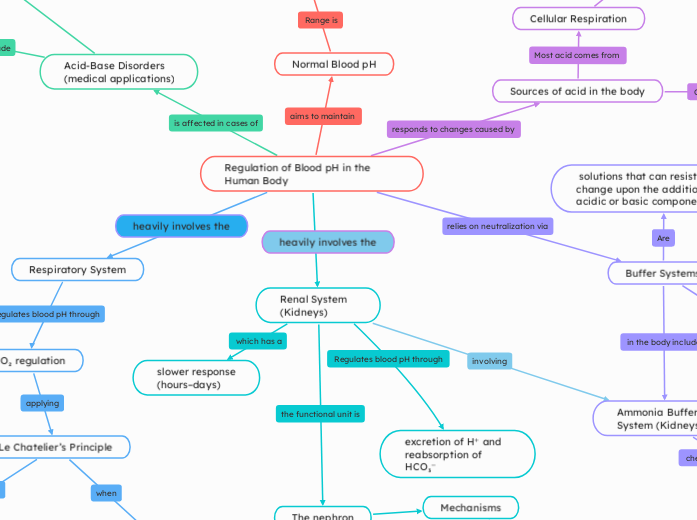
Regulation of Blood pH in the Human Body
Normal Blood pH
7.35 – 7.45 (arterial blood)
Enzyme activity
Oxygen delivery (Bohr effect)
Ionization of intermediates in biochemical pathways
Sources of acid in the body
Cellular Respiration
CO2+H2O↔H2CO3
H2CO3 ↔H+ +HCO3−
carbonic acid dissociating into bicarbonate and hydrogen ions
Other metabolic acids
Lactic acid
anaerobic exercise
Ketone bodies
fat metabolism, diabetic ketoacidosis
Dietary intake or drug metabolism
Buffer Systems
Bicarbonate Buffer System (Main System in Blood)
CO2+H2O⇌H2CO3
H2CO3⇌H++HCO3
Act instantly to resist pH changes
Phosphate Buffer System
H2PO4−⇌H++HPO42
excrete H⁺ in kidneys via NaH₂PO₄ (acidic salt)
generate new bicarbonate (Le Chatelier’s Principle)
Urine & Intracellular Fluid
Protein Buffers
Hemoglobin in red blood cells
Binds H⁺ directly
deoxygenated Hemoglobin binds more CO₂ and H⁺
Haldane Effect
Reduces Hemoglobin's affinity for O₂ (facilitates delivery)
Bohr effect
Ammonia Buffer System (Kidneys)
NH3+H+→NH4+
NH₃ freely diffuses, NH₄⁺ is trapped in urine and excreted
Generates new HCO₃⁻ for each H⁺ secreted
solutions that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components.
Respiratory System
CO₂ regulation
↑CO₂ → ↑H₂CO₃ → ↑H⁺ → ↓pH
↓CO₂ → ↓H⁺ → ↑pH
Hypoventilation (↓ breathing rate)
CO₂ accumulates
Respiratory Acidosis
Hyperventilation (↑ breathing rate):
CO₂ eliminated rapidly
Respiratory Alkalosis
Le Chatelier’s Principle
CO₂ increases, equilibrium shifts right → more H⁺ → lower pH
CO₂ decreases, equilibrium shifts left → fewer H⁺ → higher pH
Renal System (Kidneys)
excretion of H⁺ and reabsorption of HCO₃⁻
slower response
(hours–days)
The nephron
Mechanisms
Reabsorb HCO₃
Secrete H⁺
Key areas
Proximal tubule
metabolizes glutamine → 2 NH₄⁺ + 2 HCO₃⁻
Distal tubule
Collecting Duct
traps H⁺ using NH₃ →NH₄⁺ (pee)
Acid-Base Disorders
(medical applications)
Acidosis (pH < 7.35)
Metabolic Acidosis
low HCO₃⁻ or high acid
Alkalosis (pH > 7.45)
Metabolic Alkalosis
high HCO₃⁻ or low acid