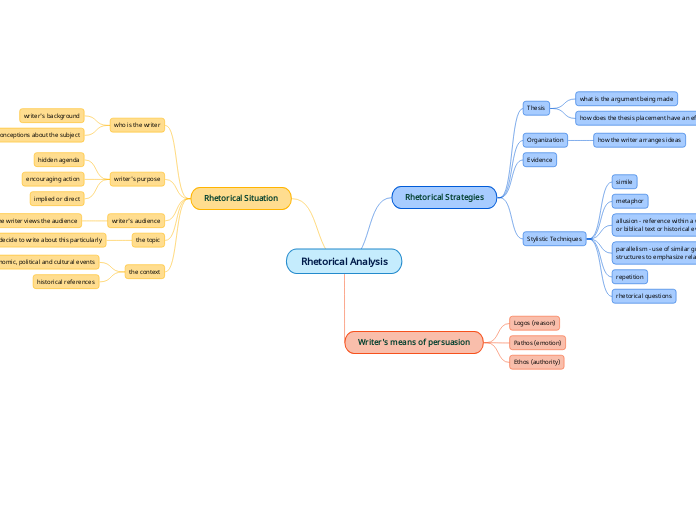
Rhetorical Analysis
Rhetorical Strategies
Thesis
what is the argument being made
how does the thesis placement have an effect
Organization
how the writer arranges ideas
Evidence
Stylistic Techniques
simile
metaphor
allusion - reference within a work to a person, literary
or biblical text or historical event to enlarge the context
parallelism - use of similar grammatical
structures to emphasize related ideas
repetition
rhetorical questions
Writer's means of persuasion
Logos (reason)
Pathos (emotion)
Ethos (authority)
Rhetorical Situation
who is the writer
writer's background
preconceptions about the subject
writer's purpose
hidden agenda
encouraging action
implied or direct
writer's audience
how the writer views the audience
the topic
why did the writer decide to write about this particularly
the context
social, economic, political and cultural events
historical references