Structural, Strength and Stability
Stability
Base Of Support
The base of support holds up a structure
For example the bases of support for a table would be the 4 legs at the bottom it keeps the table steady and stable.

Unstable
A structure that is unstable would be an object that is uneven or lop sided
For example if a table only has 1 leg for a base of support that shows that the table will topple over and be unstable.
Centre Of Gravity
If you would like a structure to be more stable the best option is for your centre of gravity to be low, rather than high
For example the more lower and wider a table is the more stable the table will be.

Stable
The centre of gravity must remain within the bases of support
For example the centre of gravity of a table is right in between the bases of support and that's how a table is stable.

Strengthening Structures
Triangles
Truss is a frame in a structure that takes advantage of the strength of triangles. A structure where many triangles are linked together. There are 3 different types of trusses: A Pratt truss: Uses right angle triangles. A Warren truss: Uses equilateral triangles or isosceles triangles. A Howe truss: Uses a variety of different triangles.
A gusset is a piece of solid material that is used to reinforce the vertices/joint in that truss.

Curves
An arch uses compression forces in order to strengthen a structure.
For example it can often be found in bridges where you have curves base supports or curves are sometimes used as doorways or entrances into buildings or structures.

Ties and Struts
Ties are a support that does it's work by resisting tension forces.
A strut resists compression forces.

Corrugation and Lamination
Corrugation is waves or a series of arches in order to increase it's stability and it is much better resisting compression then you would expect from a flat piece of paper.
Lamination is making a material thicker which will increase it's strength. Laminating paper is a plastic layer around the paper to make it more thick and water proof.

External Forces
Plane Of Application
The plane of application is that angle at which the force is applied
For example someone that is drinking from a water bottle is drinking from an ange and thats how its being used.
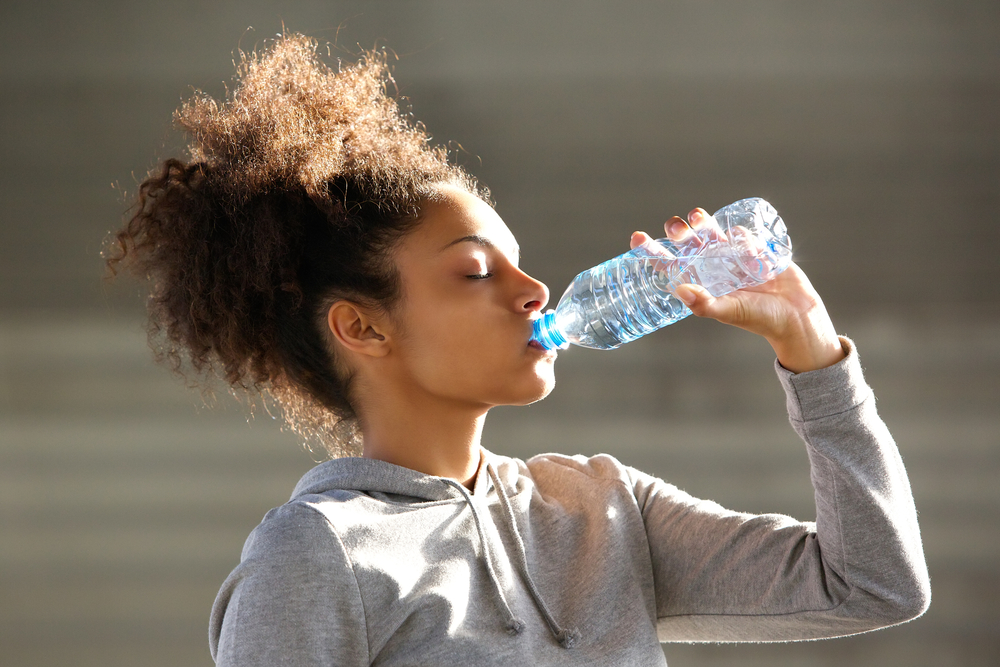

Point Of Application
The point of application is the spot on the structure that the force is being applied
For example a person picking up a water bottle would be holding it from the middle and that is where the froce is being applied.

Direction
The direction to which a force is applied is the same direction that the force is going to have an effect on
For example somebody passes a water bottle to somebody else they are pushing it at a hard speed and pushes it infront of them, that is the direction the water bottle will be going.

Magnitude
Magnitude measures how strong a force is
For example if someone would pass me a drink and they would push hard that is measuring a strong force.

Loads
Dead Load
A structure is caused by the force of gravity acting on the structure itself
For example monkey bars or a water slide can be an example of what a dead load is. A dead load is the structure itself it can't be moved.

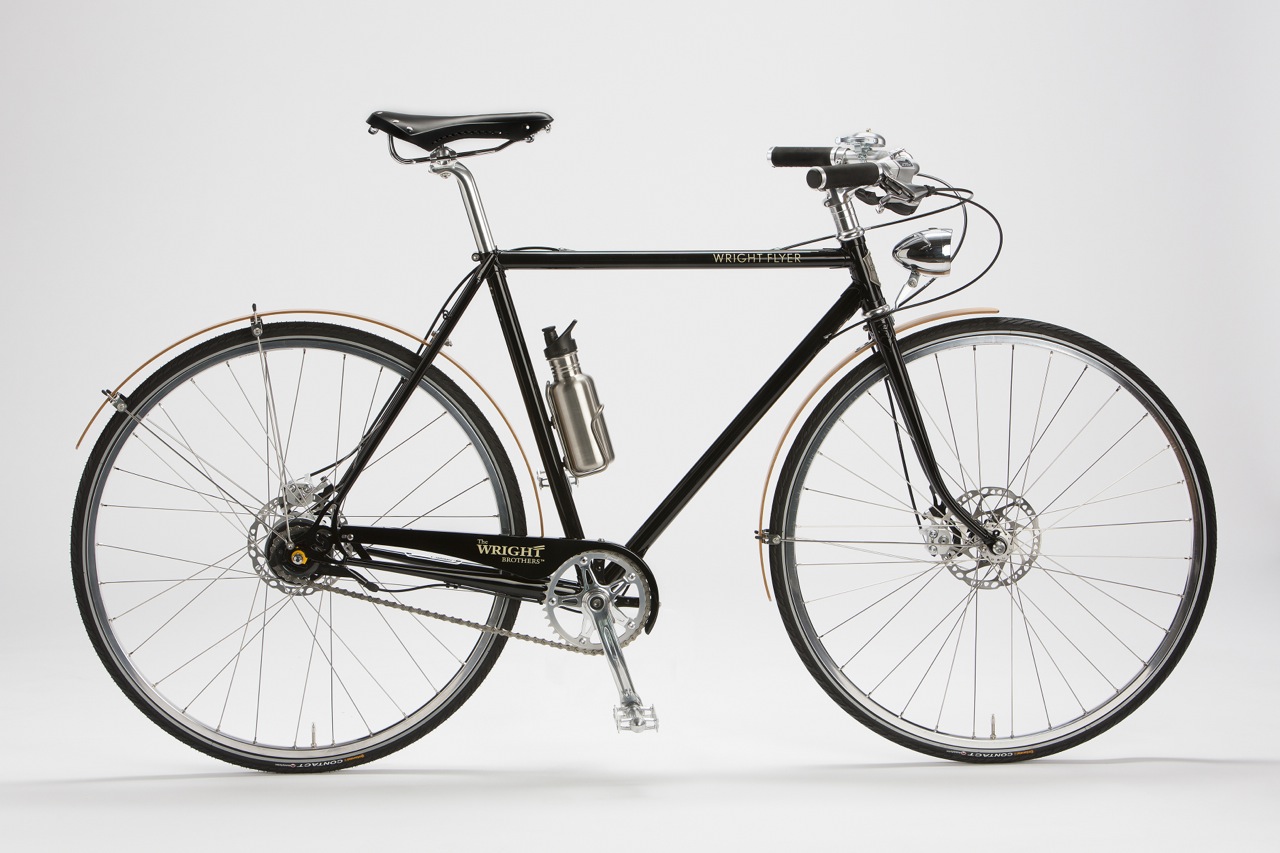
Live Load
Live load is the weight of the rider on the bicycle
For example someone riding a bike is a live load because its the weight of person. If that person gets off the bike there is no live load.

Dynamic Load
A dynamic load is a structure that doesn't have a centre of gravity and a force other then gravity
For example a dynamic load is wind or water or even any natural disaster that's cause rain, hail, or snow.

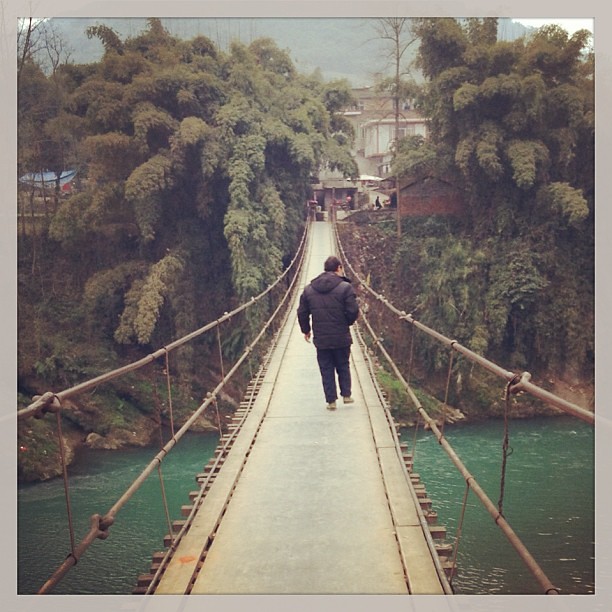
Static Load
A static load is a force due to gravity. There are two components which is dead load and live load.
Anything that goes across a bridge or is not permenetly attached to that bridge is a live load. So for example a man walking across a bridge is a static load.

Internal Forces
Compression
To squeeze or a force pushing towards eachother
For example When forces pull in opposite directions, the force of compression is created in a structure. The object responds by becoming smaller.

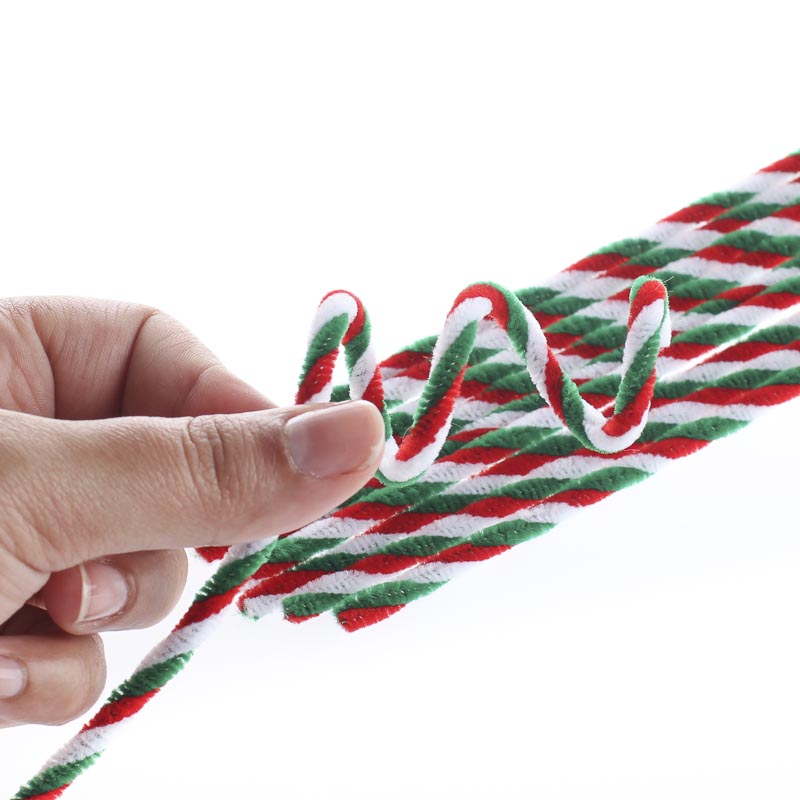
Torsion
It means to twist. When you apply a rotational force to a structure or the object s going to undergo a torsion twist
For example there are two ways that could happen: When the twisting motion is two forces in opposite directions the object is going to twist. Or... Torsion can also happen when one part of the structure's anchored and then a rotational force is applied to the other end of an anchored object.

Shear
Shear is a tearing or cutting affect on a structure.
For example when parralell forces are acting in opposite directions a shear force or a tearing is created.

Tension
It's a pulling or stretching force
For example when forces pull in opposite directions the force of tension is created in a structure. The object responds by stretching.