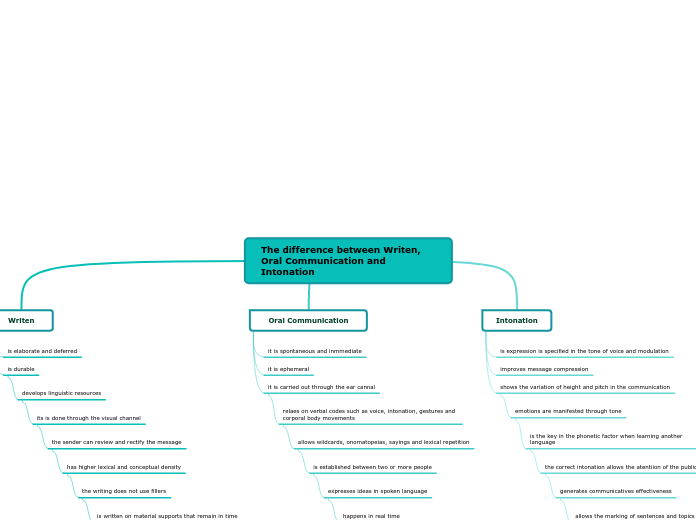
The difference between Writen, Oral Communication and Intonation
Writen
is elaborate and deferred
is durable
develops linguistic resources
its is done through the visual channel
the sender can review and rectify the message
has higher lexical and conceptual density
the writing does not use fillers
is written on material supports that remain in time
Oral Communication
it is spontaneous and inmmediate
it is ephemeral
it is carried out through the ear cannal
relaes on verbal codes such as voice, intonation, gestures and corporal body movements
allows wildcards, onomatopeias, sayings and lexical repetition
is established between two or more people
expresses ideas in spoken language
happens in real time
Intonation
is expression is specified in the tone of voice and modulation
improves message compression
shows the variation of height and pitch in the communication
emotions are manifested through tone
is the key in the phonetic factor when learning another language
the correct intonation allows the atentiion of the public
generates communicatives effectiveness
allows the marking of sentences and topics