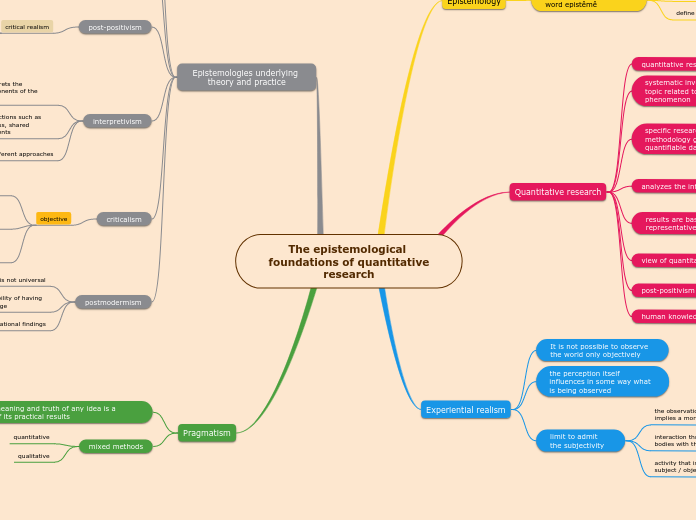
The epistemological foundations of quantitative
research
Epistemology
comes from the Greek word epistêmê
is the philosophy of knowledge
define knowledge
Quantitative research
quantitative research
systematic investigation of a topic related to a social phenomenon
specific research methodology gathering quantifiable data
using
statistical
mathematical
computational techniques
analyzes the information collected
Its purpose is to test whether a proposed study hypothesis is true or not.
results are based on larger sample sizes that are representative of the study group.
the research study can generally be replicated, simulated or repeated, due to its high reliability.
view of quantitative research
the world is seen as reality that can be empirically determined
post-positivism
experiential realism and pragmatism.
human knowledge
human conjectures
approach to reality as best they can.
Experiential realism
It is not possible to observe the world only objectively
the perception itself influences in some way what is being observed
limit to admit the subjectivity
the observation implies a more active
interaction through our bodies with the world
activity that is based on this subject / object scheme
Epistemologies underlying theory and practice
positivism
philosophical theory stating that certain ("positive") knowledge is based on natural phenomena and their properties and relations
Sensory experience, interpreted through reason and logic, constitutes the exclusive source of all true knowledge.
valid knowledge (certainty or truth) is found only in this a posteriori knowledge.
subjectivism
our own mental activity is the only unquestionable fact of our experience
Subjectivism gives primacy to subjective experience as fundamental of all measure and law.
post-positivism
critical realism
there is a reality independent of our thinking about which science can study
all observation is fallible or imperfect
prior understanding of other theories and concepts
interpretivism
interprets the components of the study
incorporates human interest in a study.
Through social constructions such as language, consciousness, shared meanings and instruments
to group different approaches
it is vital to see the differences that characterize people.
criticalism
objective
change limiting social conditions.
changing the existing and limiting social conditions
deep appreciation and appreciation of society and culture
Publicize and challenge power structures.
postmodermism
science is not universal
culture is changeable.
there is no probability of having objective knowledge
not accepting rational findings
Pragmatism
that the meaning and truth of any idea is a function of its practical results
mixed methods
quantitative
qualitative
The main advantages of quantitative approach.
Focus
approach of a scientific nature
using statistical techniques
It is an investigation on a specific problem through the application of an adopted scientific approach
analyzing
observing
counting
The use of statistical data
It can
verify
confirm
measures
researchers allow them to know how to interpret the results obtained.
definitive
reliable
standardized.
Advantage
Collect reliable and accurate data
The use of numbers makes the researchers see the subject of study represented in an impartial and precise way to analyze it objectively.
Quick data collection
The data collection methods and the way they are analyzed using statistics saves time and reduces waste of resources.
Extensive range of data analysis
Statistics as a tool, allows a broader collection of data obtained from groups of larger samples, it can be a limitation in other situations.
Eliminate bias
The results achieved are statistical.
they are verifiable.
use of a quantitative approach
simplifies
possibility of measuring
how often "situations" occur
provides larger sample size approximations
predictive generalizations of something that needs to be tested.
meaningful to draw conclusions.
optimize time and effort
in analyzing and describing the results obtained
greater precision to avoid errors and subjectivity
determine the cause and the consequence of the investigated problem.
Replicabilidad
focuses
hypothesis testing based on a well-defined plan and clear objectives
can be repeated at any other time and place obtaining the same results.
Replicabilidad
Replicabilidad
Replicabilidad