Ciencia.
Type in the name of the multiple-perspectives text.
Example: Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson
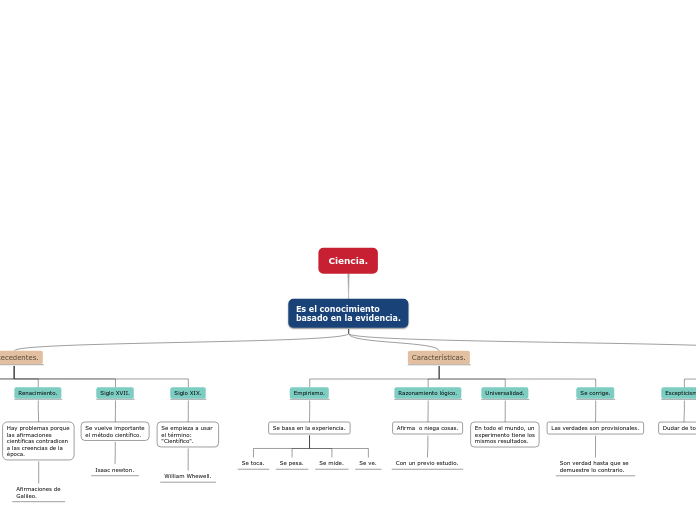
Es el conocimiento
basado en la evidencia.
Identify an important issue from the text that is being presented from different angles. Type it in.
Example: Jesse's drawing talent.
Actitudes científicas.
Whose character does the third point of view belong to?
Type in his/her name.
Example: Mr. Aarons, Jesse's father.
Curiosidad.
Seguir preguntándonos.
Para dar a más preguntas.
Apertura.
Aceptar evidencias nuevas.
Escepticismo.
What does the character think, say or do that suggests their perspective on the issue?
Type in a quote and try to maintain the citation format.
Example: 'He would like to show his drawings to his dad, but he didn't dare. (...) He'd thought his dad would be pleased. He wasn't. What are they teaching in that damn school? he had asked.' (Paterson, 2.8)
Dudar de todo.
What kind of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
Características.
Decide on the second point of view
Name the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view you are presenting.
Example: Miss Edmunds, Jesse's music teacher.
Se corrige.
Las verdades son provisionales.
Son verdad hasta que se
demuestre lo contrario.
Universalidad.
En todo el mundo, un
experimento tiene los
mismos resultados.
Razonamiento lógico.
Afirma o niega cosas.
Con un previo estudio.
Empirismo.
Type in a quote that points out the character's position about the issue.
Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'She said he was unusually talented, and she hoped he wouldn't let anything discourage him.' (Paterson, 2. 8)
Se basa en la experiencia.
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
First person point of viewSecond person point of viewThird person point of viewOmniscient point of view
Se ve.
Se mide.
Se pesa.
Se toca.
Antecedentes.
Decide on the first point of view you are going to present.
Type in the name of the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view belongs to.
Example: Jesse Oliver Aarons, Jr., the main character of the novel, a fifth-grader living in a rural Southern area.
Siglo XIX.
Se empieza a usar
el término:
"Científico".
William Whewell.
Siglo XVII.
Se vuelve importante
el método científico.
Isaac newton.
Renacimiento.
Hay problemas porque
las afirmaciones
científicas contradicen
a las creencias de la
época.
Afirmaciones de
Galileo.
Edad Media.
Se propone que el conocimiento
veraz se basa en la evidencia.
Roger Bacon.
Alzahén.
Edad Antigua.
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
Es el conocimiento
basado en la evidencia..
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
Se hacían investigaciones
del mundo natural.
What type of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
Hipatia
Aristóteles.