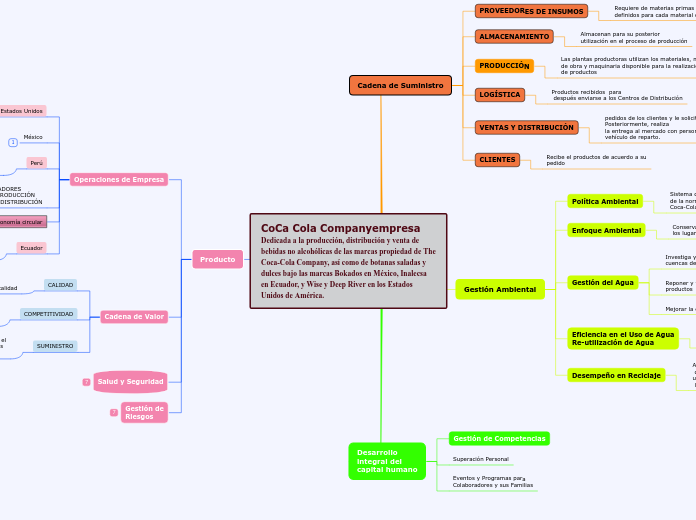
CoCa Cola Companyempresa Dedicada a la producción, distribución y venta de bebidas no alcohólicas de las marcas propiedad de The Coca-Cola Company, así como de botanas saladas y
dulces bajo las marcas Bokados en México, Inalecsa en Ecuador, y Wise y Deep River en los Estados Unidos de América.
In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order.
Producto
A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence, but a dependent clause even though it has a subject and a verb cannot stand alone.
Gestión de
Riesgos
An appositive clause follows another noun or noun phrase in apposition to it; that is, it provides information that further identifies or defines it.
SEGUROS Y FINANZAS
SEGURIDAD PERSONAL
IMAGEN Y REPUTACIÓN CORPORATIVA
SEGURIDAD DIGITAL
RIESGOS FINANCIEROS
RIESGOS OPERATIVOS
Asegurar la continuidad y sustantividad del negocio, evaluar y mitigar riesgos
Salud y Seguridad
The subject clause is a dependent clause that acts as a subject.
INFRAESTRUCTURA
• Diagnóstico
• Plan de inversión y
Mantenimiento
GESTIÓN
• Sistema de Reporte
• Comité Seguridad
• Excelencia
• Mejores Prácticas
GENTE
• Comportamiento seguro
• Capacitación
• Estructura
• Perfiles de Puesto
Garantizar la integridad
de los colaboradores
Cadena de Valor
A predicative clause may be introduced by conjunctions - that, whether, whether... or, as, as if, as though, because, lest, the way - or connectives.
The latter may be conjunctive pronouns - who, whoever, what, whatever, which - or conjunctive adverbs - where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why.
SUMINISTRO
El proveedor debe entregar en tiempo y forma el
volumen de producto o entregables de servicios
acordados.
COMPETITIVIDAD
La oferta económica del proveedor debe ser
competitiva en el mercado y se buscará que la
negociación favorezca al desarrollo de ambas partes.
CALIDAD
Entrega de productos o servicios
bajo los más altos estándares de calidad
Operaciones de Empresa
The object clause is a phrase on which a verb performs an action. It falls at the end of a sentence, and is governed by a verb or a preposition.
Ecuador
9,604 COLABORADORES
6 CENTROS DE PRODUCCIÓN
70 CENTROS DE DISTRIBUCIÓN
Convenios de impulso a la economía circular
2,095 COLABORADORES
3 CENTROS DE PRODUCCIÓN
25 CENTROS DE DISTRIBUCIÓN
Perú
4,574 COLABORADORES
6 CENTROS DE PRODUCCIÓN
72 CENTROS DE DISTRIBUCIÓN
72 CENTROS DE DISTRIBUCIÓN
6 CENTROS DE PRODUCCIÓN
4,574 COLABORADORES
México
Estados Unidos
9,419 COLABORADORES
12 CENTROS DE PRODUCCIÓN
52 CENTROS DE DISTRIBUCIÓN
Desarrollo
integral del
capital humano
A compound sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses joined by a comma, semicolon or conjunction. An independent clause is a clause that has a subject and verb and forms a complete thought.
Eventos y Programas para
Colaboradores y sus Familias
Superación Personal
Gestión de Competencias
When independent clauses are joined with coordinators (also called coordinating conjunctions), commas and semicolons, they do more than just join the clauses. They add meaning and flow to your writing.
Gestión Ambiental
Desempeño en Reciclaje
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is driving the red car.
Al disminuir la cantidad
de plástico empleado, se reduce la cantidad de energía
utilizada en los envases y mejora el procesos de
logística
Eficiencia en el Uso de Agua Re-utilización de Agua
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is driving the car with his mother.
A través del acceso a plantas de
tratamiento de aguas residuales.
Gestión del Agua
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is the driver.
Mejorar la eficiencia en el uso del agua
Reponer y tratar el agua utilizada en nuestros
productos
Investiga y participar en la protección de
cuencas de agua
Enfoque Ambiental
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives the car.
Conservación de los recursos de
los lugares en que opera
Política Ambiental
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives.
Sistema de Administración Ambiental, basado en los requisitos de la norma ISO 14001 y los Requerimientos Operativos de Coca-Cola (KORE)
Cadena de Suministro
CLIENTES
An adverbial is an individual word (that is, an adverb), a phrase, or a clause that can modify a verb, an adjective, or a complete sentence.
Recibe el productos de acuerdo a su
pedido
VENTAS Y DISTRIBUCIÓN
The attribute is defined as a quality or characteristic of a person, place or thing.
pedidos de los clientes y le solicita al área de logística, Posteriormente, realiza
la entrega al mercado con personal a bordo de un
vehículo de reparto.
LOGÍSTICA
The predicative is defined as an adjective or noun forming or contained in the predicate.
Its main trait is that it serves to express a property that is assigned to a 'subject'.
For e.g.: The dog is old.
Productos recibidos para
después enviarse a los Centros de Distribución
PRODUCCIÓN
Traditional grammar defines the object in a sentence as the entity that is acted upon by the subject.
Las plantas productoras utilizan los materiales, mano
de obra y maquinaria disponible para la realización
de productos
The direct object is the receiver of the action mentioned in the sentence.
ALMACENAMIENTO
The predicate of a sentence is the part that modifies the subject in some way. Because the subject is the person, place, or thing that a sentence is about, the predicate must contain a verb explaining what the subject does and can also include a modifier.
Almacenan para su posterior
utilización en el proceso de producción
PROVEEDORES DE INSUMOS
The subject of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb.
Ask the question, 'Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?' and the answer to that question is the subject.
Requiere de materias primas que deben seguir estándares
definidos para cada material que son enviados en unidades