structure + function of polysaccharides determined by sugar monomer and type of glycosidic linkage
structure (e.g. cellulose, chitin)
hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases
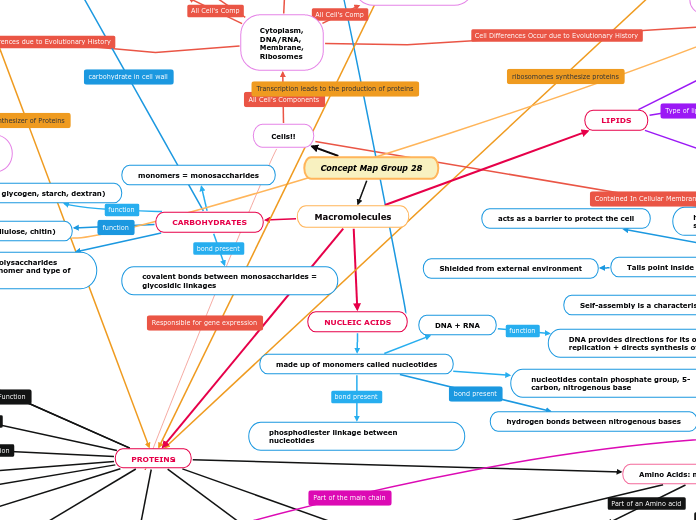
LIPIDS
regulates membrane fluidity, component of hormones
contain 4 fused rings
Steroids
energy storage
glycerol and fatty acid linked by ester linkages
Fats (triacylglycerol)
Golgi Apparatus- Modifies proteins and involved in intercellular transport
Centrosomes- regulates cell motility & adhesion and polarity in interphase,
Vacuole- Animals have small vacuoles that mainly hold organic molecules and are responsible for transport through the plasma membrane.
Lysosome- digestive system of the cell, serving both to degrade material taken up from outside the cell and to digest obsolete components of the cell itself.
Cell Wall- Holds the plants together when exposed to hypotonic solutions that would otherwise burst the cell, making it 'turgid.'
Nucleus- Hold's genetic info, keep DNA integrity, and conduct replication & transcription
Plant
Central Vacuole- Unlike animal cells, plant cells have a large vacuole in the middle of the cell that holds a large amount of water.
Chloroplast- convert light energy into chemical energy via the photosynthetic process, contains plastids, and has its own DNA.
Endosymbiotic Theory- The beginning of eukaryotic cells organelle. Such as mitochondria and plastids, evolved from free-living prokaryotes that were consumed and formed a symbiotic with the cell that ate them. This is supported by the fact that Mitochondria and Chloroplast have their own separate DNA
Animal
Same Organelles in Both Types of Eukaryotes & Their Functions
Mitochondria- Responsible for making ATP and is double-membraned and has its own DNA
Rough ER- Ribosomes attached to wall that synthesize proteins
Smooth ER- Synthesizes lipids and detoxifies cells
Vacuole- Hold important organic materials or hold waste materials inside of cell's
Ribosomes Function - Synthesizing proteins
Membrane Bound Nucleus
Cell Wall made of Peptidoglycan (In Bacteria)
No Membrane Bound Nucleus
Chromosomes are Circular and float around in cytoplasm instead of a nucleus.
PROTEINS
Amino Acids: monomer in proteins
Hydrogen
R Group
Carboxyl group
Amino group
Response of cell to chemical stimuli
Coordination of an organism's activities
Transports of substances
Carrier proteins
Storage of amino acids
Protection against disease
Subtopic
Selective acceleration of chemical reactions
Enzyme
Quaternary
Two polypeptides in tertiary level, interacting with R groups
Tertiary
Forms final 3D shape
Folds through interaction of R groups
Basic
Ion dipole: Complete positive charge with water bond
Acidic
Hydrophilic
Polar Bonds
Non Polar Bonds
Hydrophobic interactions
Secondary
Alpha helices
Beta Plated Sheets
Primary
Polypeptide
Uses main chain to form bonds
Intramolecular Bonds: Covalent
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
imperative for cell life
linked to signal transductions
& organelle functions
& physiological processes
& human diseases
Each phospholipid has a specific transition temperature
goes into a liquid crystalline phase when the temperature is exceeded
phospholipids move rapidly when fluid
movement in membranes is regulated by the cholesterol in membranes
movement is reduced as temperature decreases
when this happens the membrane becomes more gel-like.
Bilayer forms by self assembly when contact is made with water
Self-assembly is a characteristic feature
acts as a barrier to protect the cell
Form because of their amphiphilic characteristics
hydrophilic heads make all contact with the solution
Tails point inside
Shielded from external environment
Two fatty acids attached to glycerol
Non polar hydrophobic tails
The type of hydrocarbon tails effects the plasma membrane fluidity
glycerol attaches to a phosphate group
polar hydrophilic head
hydrophilic because of the phosphate group
Exhibits negative charge within cell
Soluble in non polar solvents
Hydrophobic behavior
A type of lipid, one of the most important components of biochemistry
Major component of the cell membrane
impart selective permeability
they control the movement of molecules across the cell membrane
Membranes have saturated and unsaturated fatty acids to maintain the proper amount of fluidity
responsible for dynamic membrane fluctuations
Cytoplasm, DNA/RNA, Membrane, Ribosomes
Cellular Membrane- Semi-permeable barrier that allows essential molecules into the cell for use
DNA/RNA - Genetic material that's responsible for longterm storage of cellular information
Cytoplasm- Gel-like substance that is a medium for chemical reactions in cell
Prokaryotes (Archaea & Bacteria)
Capsules- Helps prokaryotes cling to each other and to various surfaces in their environment
Plasmids - genetic structure in a cell that can replicate independently of the chromosomes.
Eukaryotes
Membrane Bound Organelles
Cell Wall (if any) made of cellulose (or chitin in fungus)
Cells!!
Concept Map Group 28
Macromolecules
CARBOHYDRATES
storage (e.g. glycogen, starch, dextran)
covalent bonds between monosaccharides = glycosidic linkages
monomers = monosaccharides
NUCLEIC ACIDS
made up of monomers called nucleotides
DNA + RNA
DNA provides directions for its own replication + directs synthesis of mRNA
phosphodiester linkage between nucleotides
nucleotides contain phosphate group, 5-carbon, nitrogenous base