realizată de Simmi Sekhon 5 ani în urmă
452
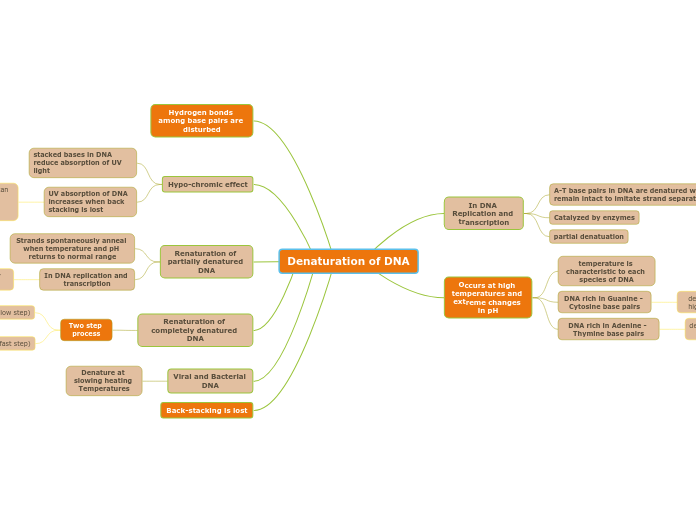
Denaturation of DNA
realizată de Simmi Sekhon 5 ani în urmă
452

Mai multe ca acesta
Type in the name or subject of your brainstorming
spontaneous annealing of unpaired bases
By random collisions strands find each other