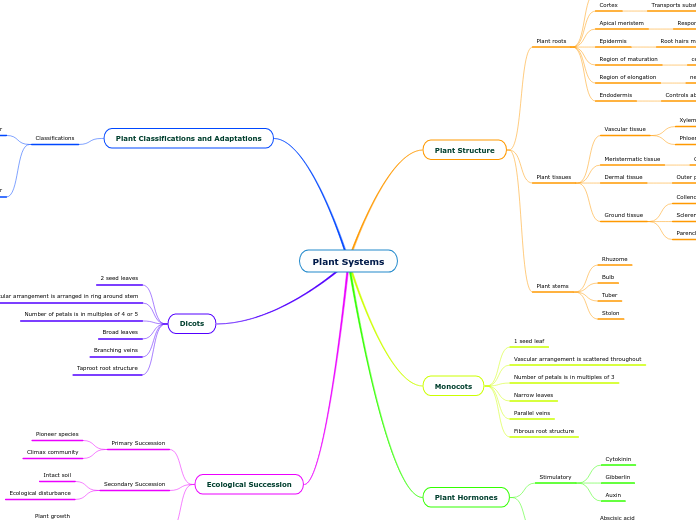
Plant Systems
Ecological Succession
Ecological Disturbance
Increased diversity
Plant growth
Secondary Succession
Ecological disturbance
Intact soil
Primary Succession
Climax community
Pioneer species
Dicots
Taproot root structure
Branching veins
Broad leaves
Number of petals is in multiples of 4 or 5
Vascular arrangement is arranged in ring around stem
2 seed leaves
Plant Classifications and Adaptations
Classifications
Non-vascular
No flowers, leaves, roots or stems
Vascular
Gymnosperm
Don't produce seeds
Cone bearing
Angiosperm
Bears fruits
Dicot
Monocot
Plant Hormones
Inhibitory
Ethylene
Abscisic acid
Stimulatory
Auxin
Gibberlin
Cytokinin
Monocots
Fibrous root structure
Parallel veins
Narrow leaves
Number of petals is in multiples of 3
Vascular arrangement is scattered throughout
1 seed leaf
Plant Structure
Plant stems
Stolon
Tuber
Bulb
Rhuzome
Plant tissues
Ground tissue
Parenchyma
Sclerenchyma
Collenchyma
Dermal tissue
Outer protective layer of the primary plant body
Meristermatic tissue
Cells that have the ability to divide
Vascular tissue
Phloem
Xylem
Plant roots
Endodermis
Controls absorption of water and nutrients
Region of elongation
new cells begin to increase in length
Region of maturation
cells mature into various tissues
Epidermis
Root hairs maximize water absorption
Apical meristem
Responsible for extension of roots and shoots
Cortex
Transports substances between vascular and epidermis
Root cap
Reduces friction and protects root when growing